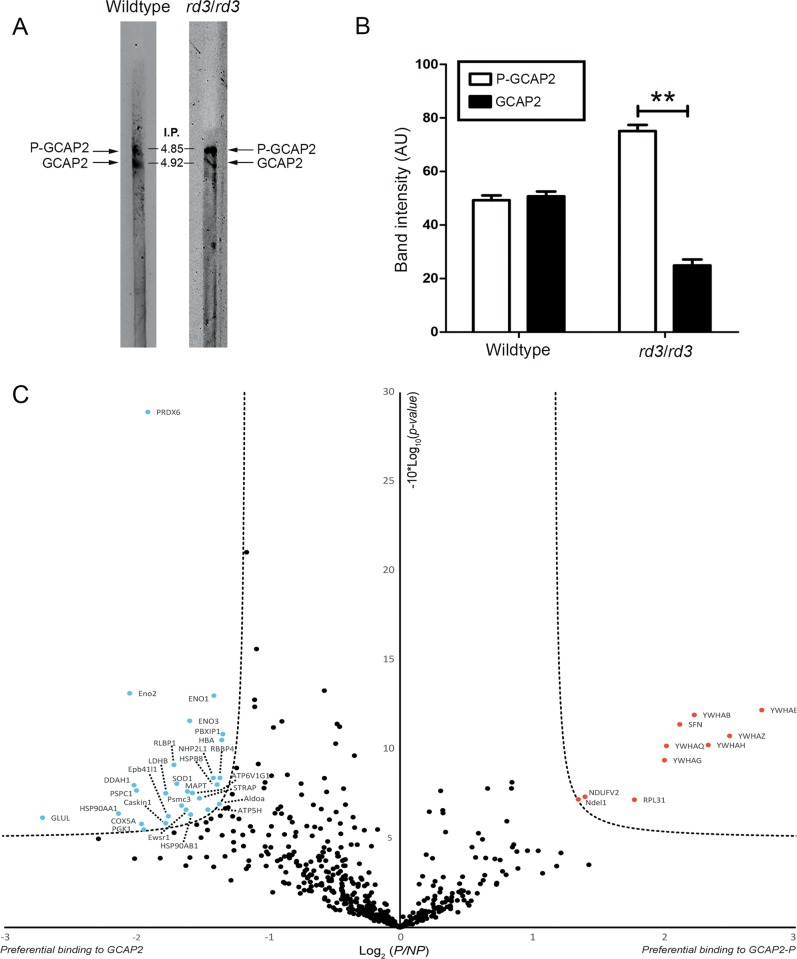
Fig. 5. GCAP2 in rd3/rd3 retinas is largely in its Ca2+-free-phosphorylated state, which is a target for 14-3-3 binding.
a Isoelectric focusing (IEF) separation of retinal homogenates from wt and rd3/rd3 mice at p30 in linear pH 3–10 gradient gel strips. Following IEF, proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and immunoblotted with anti-GCAP2 pAb. b The GCAP2-P to GCAP2 ratio was determined by densitometric analysis (mean ± SEM) of three independent isoelectrofocusing experiments. Unpaired t-test (GCAP2 versus GCAP2-P in wt mice, P = 0.72) and (GCAP2 versus GCAP2-P in rd3 mice, P = 0.0082**). c Label-free quantitative proteomic analysis to identify putative protein interactions of Ca2+-free GCAP2-P and GCAP2. Pull-down assays were performed on bovine retinal homogenates with purified myristoylated GCAP2 that was phosphorylated in vitro or a MOCK-phosphorylation control, under EGTA conditions. The volcano plot represents the statistical analysis of three independent pull-down assays. Log2 (P/NP) refers to Log2 (Mean NSAFGCAP2-P/Mean NSAFGCAP2), with NSAF being the normalized spectral abundance factor, see Methods section. The already reported 14-3-3 phosphobinding proteins (different isoforms) were clearly revealed as Ca2+-free GCAP2-P interactors, validating the assay. Other putative interactors identified with statistical significance are marked in red (GCAP2-P) and blue (GCAP2). The whole list of identified proteins is provided in Supplementary Table 1.