Fig. 8. Sketch summarizing the mechanisms that likely contribute to the physiopathology of rd3 mice and LCA12 patients.
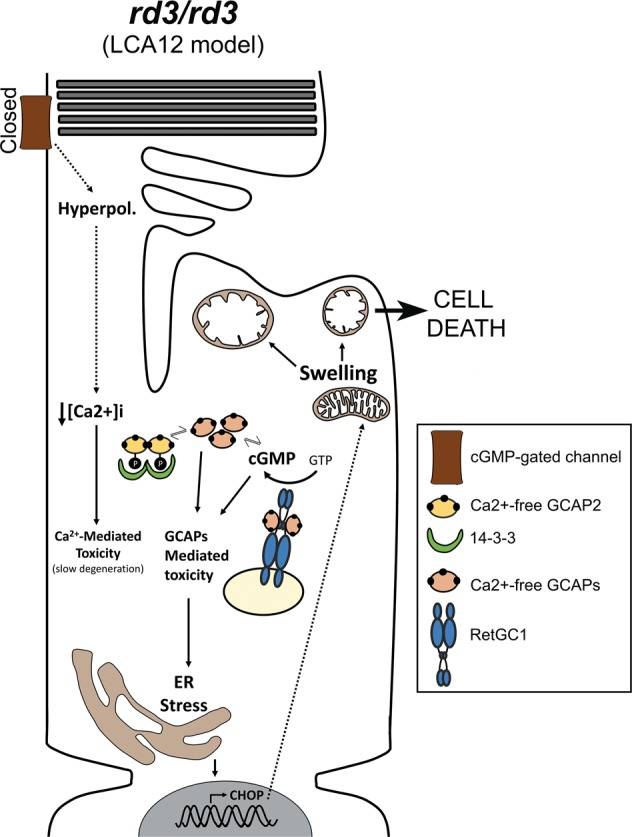
The lack of RD3 represents an immediate insult for photoreceptor cells by causing chronic hyperpolarization and chronic low [Ca2+]i due to the closure of CNG-channels by the severe drop in cGMP synthesis. This chronic low [Ca2+]i likely represents the original insult causing damage to the cell. Chronic low Ca2+ cause the GCAP proteins to remain permanently in their Ca2+-free conformation. GCAPs in their Ca2+-free guanylate cyclase activator state in the absence of RD3 may stimulate cGMP synthesis at the inner segment, ultimately causing ER stress and ER stress-mediated apoptosis. Ca2+-free GCAP2 conformational instability may also ultimately induce ER stress. GCAP2 phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding might serve a protective role from both pathways of damage.
