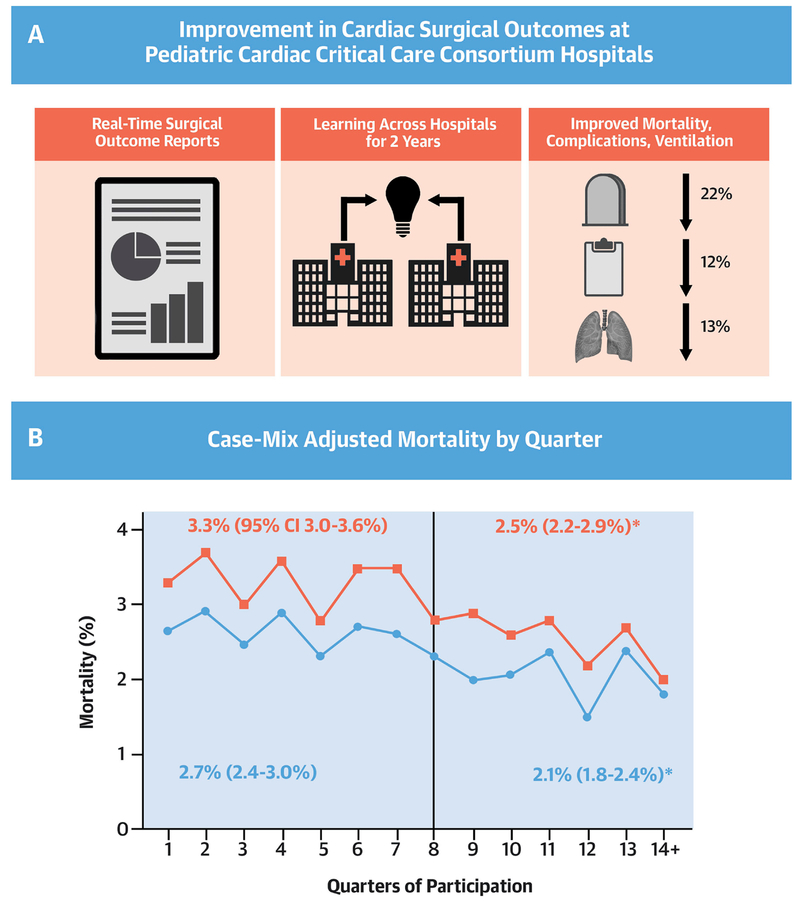
Central Illustration: Improving Pediatric Cardiac Surgical Outcomes: Change in Postoperative Mortality Over Time.
Panel A: Improvement in cardiac surgical outcomes at pediatric cardiac critical care consortium hospitals. Panel B: Case mix adjusted mortality by quarter. Vertical line represents end of baseline period. Blue line and squares represent in-hospital mortality. Red line represents cardiac ICU postoperative mortality. The relative decrease in the post-exposure period for in-hospital mortality and cardiac ICU mortality was 24% (2.7% mortality during baseline vs. 2.1% post-exposure) and 22% (3.3% vs. 2.5%), respectively.
† p<0.05 for comparison of baseline vs. post-exposure rates. CI, confidence interval.
Gaies, M. et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(22):2786-95.