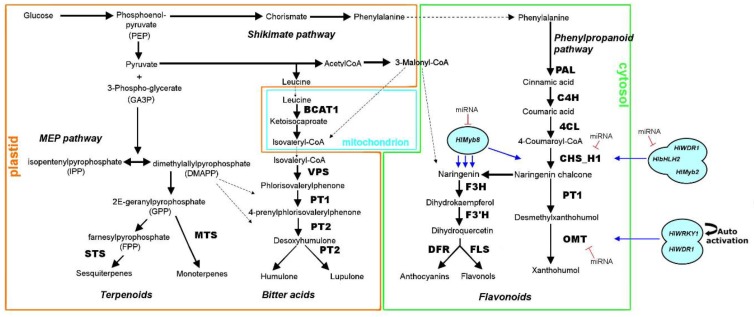
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the biosynthetic pathways (terpenoids, bitter acid, phenylpropanoids and flavonoid) in the hop. The methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway leading to DMAPP biosynthesis contributes to the bitter acid and terpenoids biosynthesis. Bitter acids are formed from acyl-CoA precursors derived from branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) degradation and MEP pathway. The prenylated chalcones (xanthohumol) biosynthesized via shikimate pathway. The main intermediate compounds are shown with the abbreviation of respective enzymatic steps. Enzyme abbreviations are PAL: phenylalanine ammonia lyase; C4H: cinnamate 4-hydroxylase, 4CL: coumarate coenzyme A ligase, CHS: chalcone synthase, PT: prenyltransferase; OMT: O-methyltransferases; VPS: valerophenone synthase, BCAT: branched chain aminotransferase; F3H: flavanone 3-hydroxylase; F3′H, flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase; DFR, dihydroflavonol 4-reductase; FLS: flavonol synthase; STS: Sesquiterpene synthase; MTS: monoterpene synthases. OMTI and CHS_H1 represent gene isoforms of O-methyltransferases and chalcone synthase genes, respectively in the hop. The movement of metabolic intermediates between cellular compartments is indicated by dashed line.