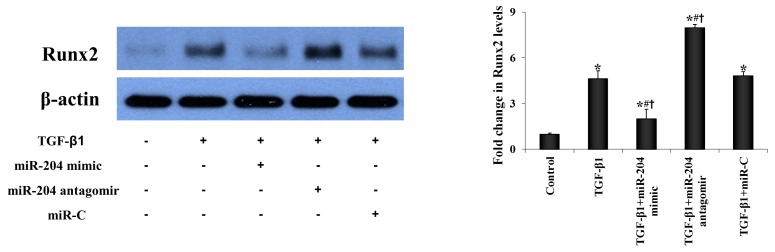
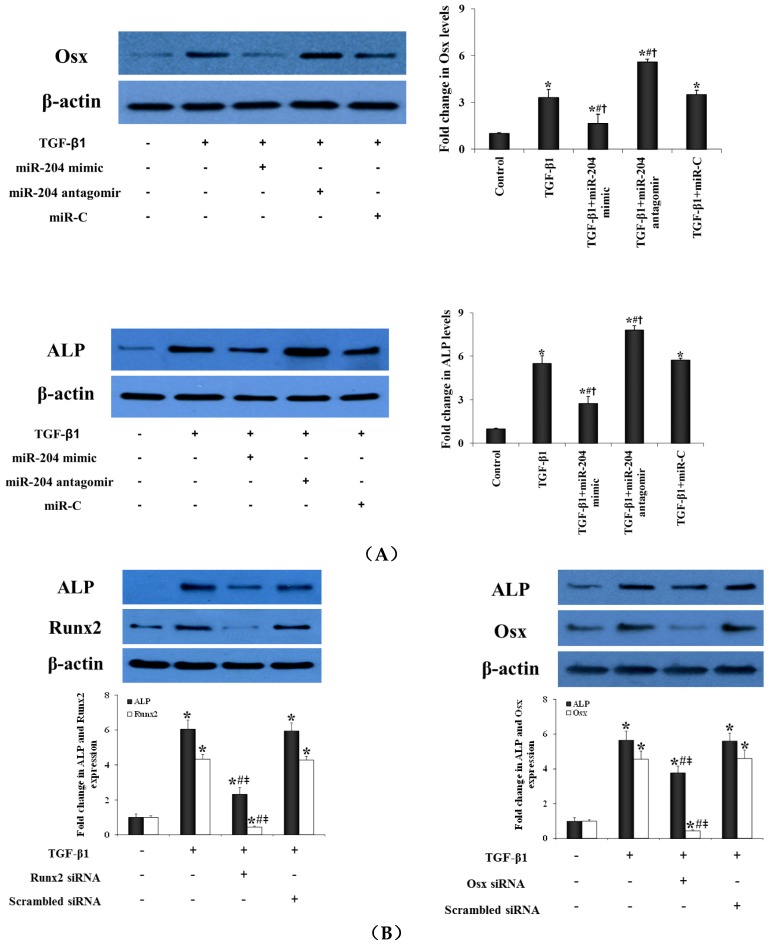
Figure 4.
MiR-204 down-regulates the expression of both Runx2 and Osx expression in human AVICs to suppress pro-osteogenic reprogramming. (A) AVICs from normal aortic valves were treated with miR-204 mimic (5 nM), antagomir (50 nM) or irrelevant oligonucleotide (miR-C, 50 nM) for 24 h and then stimulated with TGF-β1 (0.005 μg/mL) for 24 to 48 h. Representative immunoblots and densitometric data show that miR-204 mimic suppressed, but miR-204 antagomir enhanced the expression of Runx2 and Osx at 24 h, as well as the levels of ALP at 48 h following treatment with TGF-β1. Mean ± SE; n = 6 distinct cell isolates; * p < 0.05 vs. untreated control; # p < 0.05 vs. TGF-β1 alone; † p < 0.05 vs. TGF-β1+miR-C. (B) AVICs from normal aortic valves were treated with specific siRNA (100 nM) for 48 h to knockdown Runx2 or Osx and then stimulated with TGF-β1 (0.005 μg/mL) for 48 h. Controls were pre-treated with scrambled siRNA (100 nM) and then stimulated with TGF-β1. Representative immunoblots and densitometric data show that knockdown of Runx2 markedly reduced the effects of TGF-β1 on ALP levels, whereas knockdown of Osx had a moderate effect. Mean ± SE; n = 6 distinct cell isolates; * p <0.05 vs. untreated control; # p < 0.05 vs. TGF-β1 alone; ≠ p < 0.05 vs. TGF-β1+scrambled siRNA.