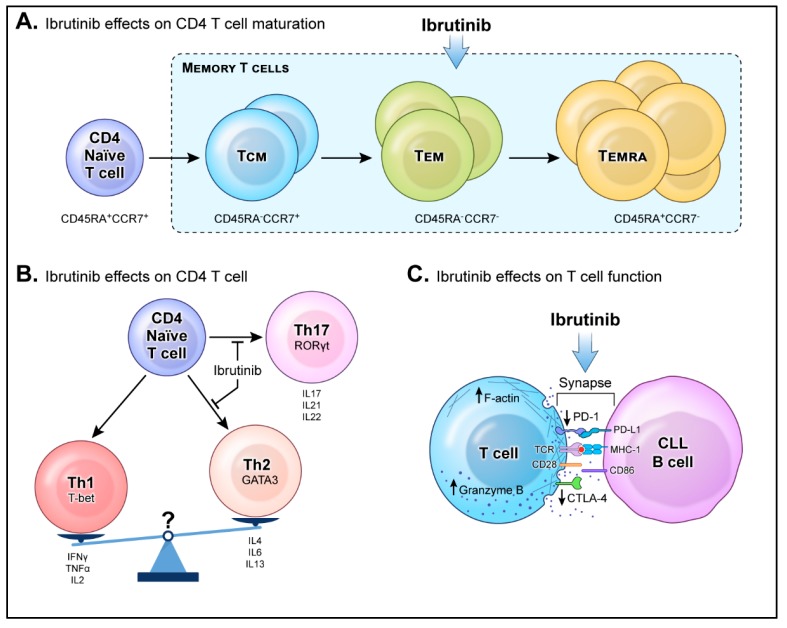
Figure 1.
Ibrutinib shifts T-cell differentiation and function towards improved antitumor control, immunity and surveillance. This figure summarizes the reported effects of ibrutinib on T cells: (A) Ibrutinib affects the differentiation of naive CD4 T cells into memory T cells. After ibrutinib treatment, more differentiated memory T cells, including central memory (CM), effector memory (EM) and effector memory RA (EMRA), are increased; (B) Ibrutinib affects the differentiation of naive CD4 T cells into T helper cells shown by changes of different Th-mediated cytokines in serum or plasma of treated patients. Ibrutinib inhibits the polarization into Th17 and Th2 cells; the latter results in a shift towards Th1 and favors antitumor immunity; (C) Treatment with ibrutinib also repairs immune synapse formation between T cells and CLL cells by enhancing F-actin polarization and granzyme B production and decreasing the expression of inhibitory receptors such as PD-1 and CTLA4.