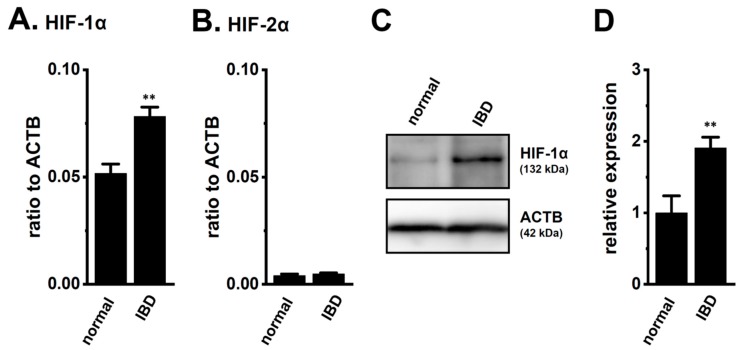
Figure 1.
Increased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α in the splenic CD4+ T cells of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) model mice. (A,B) Real-time PCR assay for HIF-1α (A) and -2α (B) in the splenic CD4+CD25− T cells of ‘normal’ and ‘IBD’ model mice (n = 4). Expression levels are shown as a ratio to β-actin (ACTB). (C,D) HIF-1α protein expression (132 kDa) in the splenic CD4+ T cells of ‘normal’ and ‘IBD’ model mice. Protein lysates of the examined cells were probed by immunoblotting with anti-HIF-1α (upper panel) and anti-ACTB (42 kDa, lower panel) antibodies on the same filter (C). Summarized results were obtained as the optical density of HIF-1α and ACTB band signals (D). After compensation for the optical density of the HIF-1α protein band signal with that of the ACTB signal, the HIF-1α signal in ‘normal’ mice was expressed as 1.0 (n = 4). Results are expressed as means ± SEM. **: p < 0.01 vs. normal mice (normal).