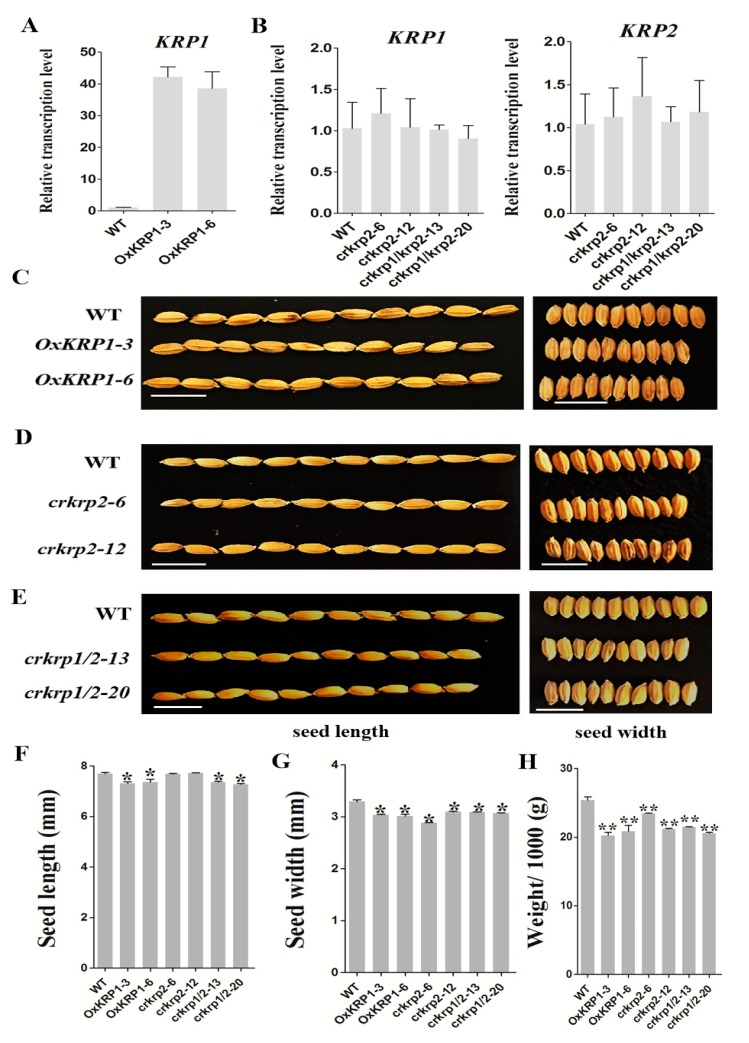
Figure 2.
Phenotypic characteristics of OxKRP1, crkrp2, and crkrp1/2 mature seeds. (A) qRT-PCR analysis for transcript accumulation of KRP1 in the 6 DAP developing seeds of OxKRP1 transgenic lines. Error bars indicate the SD with biological triplicates (n = 3); (B) qRT-PCR analysis for transcript accumulation of KRP1 and KRP2 in the 6 DAP developing seeds of crkrp2 and crkrp1/2 mutants. Error bars indicate the SD with biological triplicates (n = 3); (C) comparison of mature seeds of the WT and OxKRP1 plants. OxKRP1-3 and OxKRP1-6 represent two independent KRP1-overexpressing lines, respectively; and (D) comparison of mature seeds of the WT and crkrp2 plants. crkrp2-6 and crkrp2-12 represent two independent crkrp2 mutants, respectively; (E) comparison of mature seeds of the WT and crkrp1/2 plants. crkrp1/2-13 and crkrp1/2-20 represent two independent crkrp1/2 double mutants, respectively; (F–H) seed length, seed width and 1000-seed weight of the WT, OxKRP1, crkrp2, and crkrp1/2 mature seeds. Error bars indicate the SD with 50 biological replicates (n = 50). Asterisks indicate the significant difference between the WT and transgenic lines, as determined by Student’s t-test analysis: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. WT: wild type, Bar = 1 cm in (C–E).