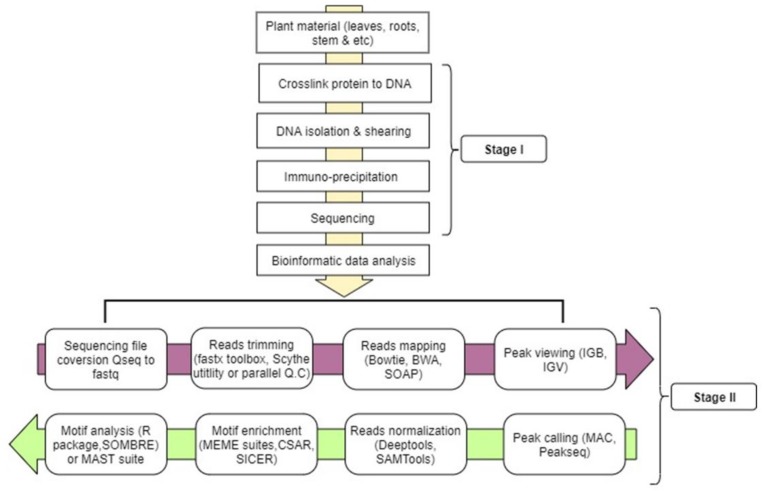
Figure 2.
Basic steps involved in ChIP-seq: stage I starts from crosslinking to sequencing and stage II involves steps for gene mining. Sequenced file Qseq are converted to fastq format using fastx tools, reads undergo trimming and filtering using Scythe utility or parallel Q.C, then reads alignment using Bowtie or Burrow Wheelers alignment (BWA), matched reads viewing is aided by integrative genome browser (IGB). Peaks are called using any available software like MAC/Peakseq, reads are normalized by removing duplicate reads and searching for tag densities in a window of reads per kilobase per million reads (RPKM) around the reference peak, mostly 1 kb upstream of transcription start site (TSS) to transcription end site (TES), with SAMTools, motif search using MEME suites, and finally predicts gene through MAST suite or R statistic package SOMBRE with the aid of GO and transcription factor databases like JASPAR.