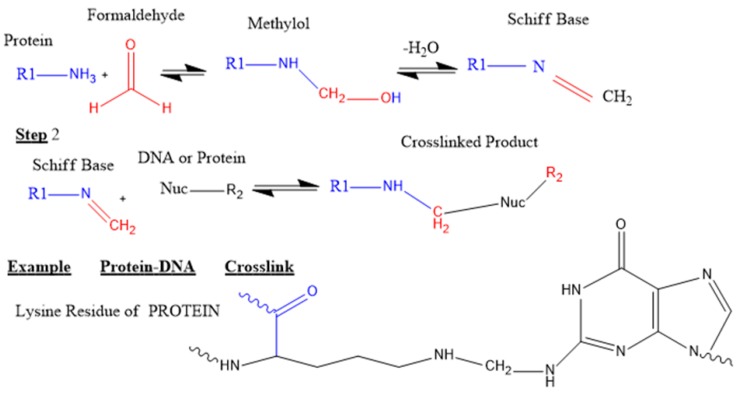
Figure 3.
Chemical reactions of protein–DNA crosslinking by formaldehyde: Crosslinking of protein–DNA by formaldehyde occurs in two steps. Firstly, a strong nucleophile, commonly a lysine є-amino group from a protein, reacts with formaldehyde to form a methylol intermediate which will lose water to give a Schiff base (an imine). Secondly, the Schiff base reacts with another nucleophile amine of a DNA to generate a crosslinked product. The latter nucleophile might also be from another protein or the same protein as the first nucleophile. All the reactions in this stoichiometric process are reversible. Modified from Hoffman et al. (2015) [97].