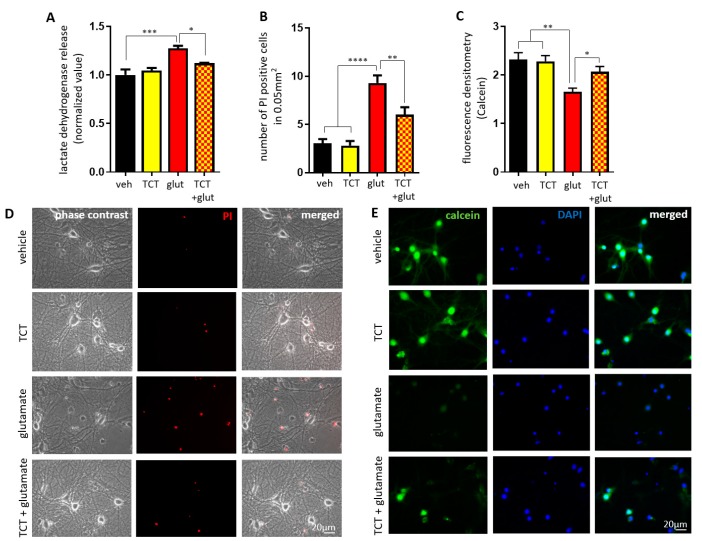
Figure 1.
α-tocotrienol (TCT) protects against glutamate-induced death in primary hippocampal neurons. Primary hippocampal neurons were treated with α-TCT (1 µM), glutamate (20 µM), or a combination of both for 24 h. Quantified neuronal toxicity, death, and viability were measured by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release (n = 3 from three independent cultures) (A), PI positive cells (n = 20 micrographs per group) (B), and calcein retention (n = 35–39 micrographs per group) (C), respectively. PI-stained dead cells (D) or calcein-stained live cells (E) were imaged using a 32× fluorescent microscope. Hippocampal neurons treated with α-TCT were protected from glutamate-mediated death (Red: PI; green: calcein; blue: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, DAPI). Scale bar = 20 µm. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA.