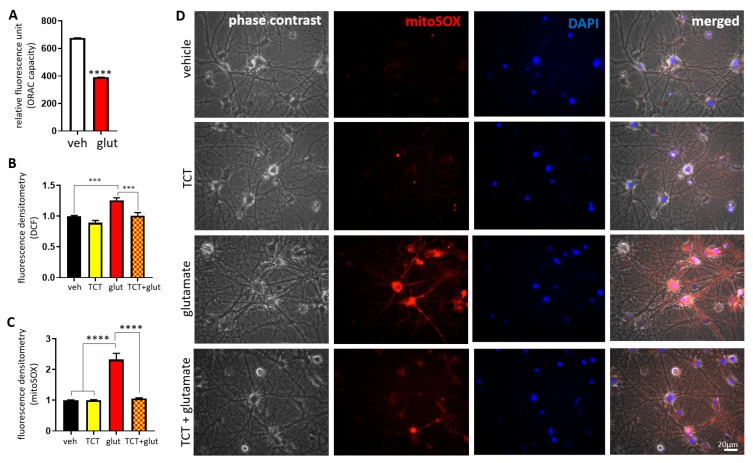
Figure 2.
α-TCT attenuates glutamate-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in the mitochondria. Primary hippocampal neurons were treated with α-TCT (1 µM), glutamate (20 µM), or a combination of both for 6 h. Quantification of intracellular lipophilic antioxidant capacity (A) and oxidative stress level (B) were assayed by measuring fluorescence intensity of fluorescein and 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein (DCF) using the whole cell body (A, n = 6; B, n = 12), respectively. Mitochondrial oxidative stress levels were measured by mitoSOX staining. (C) Fluorescent intensity of mitoSOX (n = 15). (D) Glutamate treatment significantly increased fluorescence intensity of mitoSOX, whereas mitoSOX signal was attenuated by α-TCT co-treatment in primary hippocampal neurons (Red: mitoSOX; blue: DAPI). Scale bar = 20 µm. *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA.