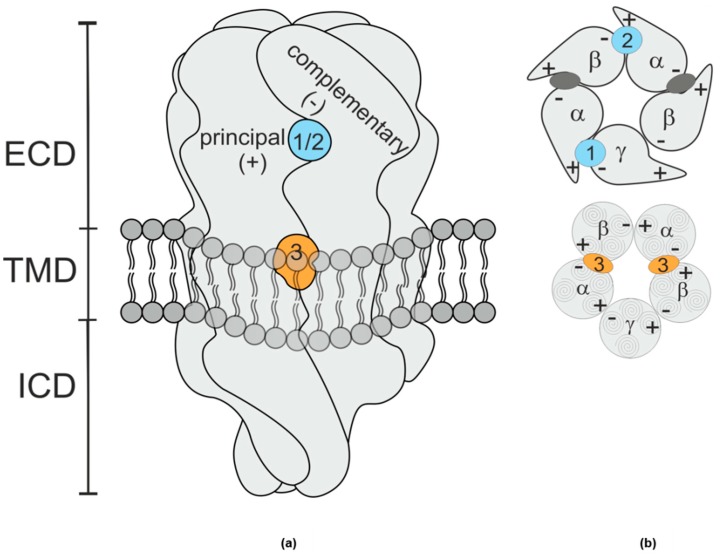
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic rendering of a GABAA receptor. The extracellular domain (ECD) and transmembrane domain (TMD) contain various binding sites [11]. The binding sites studied in this work are at interfaces formed by a principal (+) subunit face and a complementary (−) subunit face. The shape resembles vaguely a space filling rendering of the protein’s ECD and TMD, while intracellular domain (ICD) shape is a purely schematic rendering based on more remote homologues. (b) Schematic planes through the ECD (top) and TMD (bottom) of a canonical αβγ receptor, the GABA sites are indicated as dark grey ellipses. Site 1 (blue), the high affinity benzodiazepine site, is at the ECD– α+/γ− interface; site 2 (blue), which confers modulatory effects of pyrazoloquinolinone ligands is at the ECD– α+/β− interface, and site 3 (orange), the etomidate site [7] occurs twice and is located at the TMD– β+/α− interfaces below the GABA binding sites.