Figure 2.
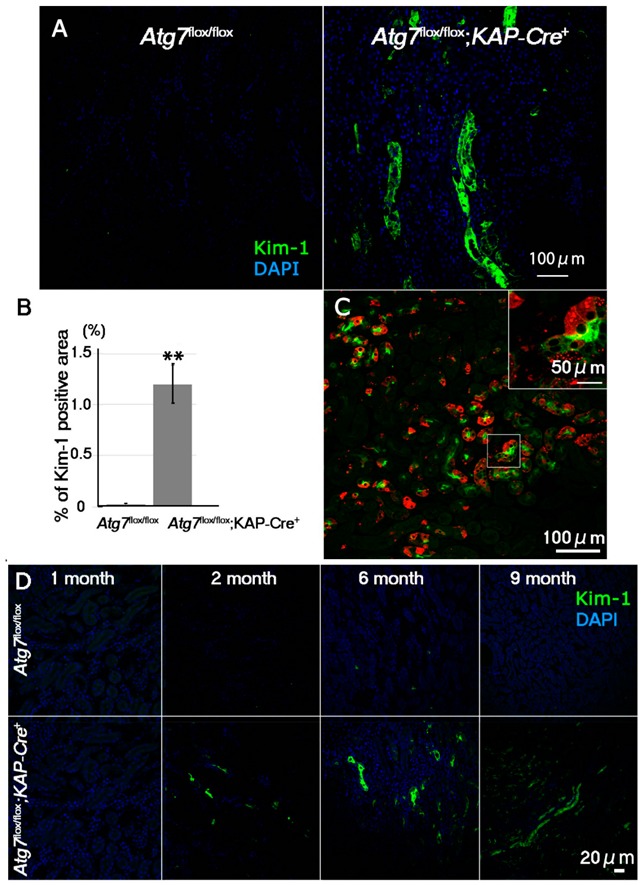
Age-dependent increase of Kim-1, a marker for early kidney injury, in the Atg7flox/flox;KAP-Cre+ mouse kidney. (A) Representative images of Kim-1 immunostaining (green) in the proximal region of the kidneys of 2-month-old Atg7flox/flox;KAP-Cre+ mice. As a control, Atg7flox/flox mouse kidneys were used. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (B) Quantification of Kim-1-positive area of 2-month-old Atg7flox/flox and Atg7flox/flox;KAP-Cre+ mouse kidneys. Kim-1-positive signals in the cortico-medullary region of 2 month-old Atg7flox/flox (n = 4) and Atg7flox/flox;KAP-Cre+ (n = 7) mice were estimated by ImageJ software (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/index.html) [26]. Statistical analyses were performed using a student’s t-test (** p < 0.03). Data in the graph are expressed as the mean ± SEM. (C) Accumulation of Kim-1-positive signals in p62-positive autophagy-deficient renal tubular cells. Renal tubular cells in the cortico-medullary region were detected anti Kim-1 (green) and p62 (Red). (D) Age-dependent accumulation of Kim-1 in Atg7flox/flox;KAP-Cre+ mouse kidney. Kidney samples from 1-, 2-, 6-, and 9-month-old Atg7flox/flox;KAP-Cre+ (lower) and Atg7flox/flox (upper) mice were stained with anti-Kim-1 antibody (green).
