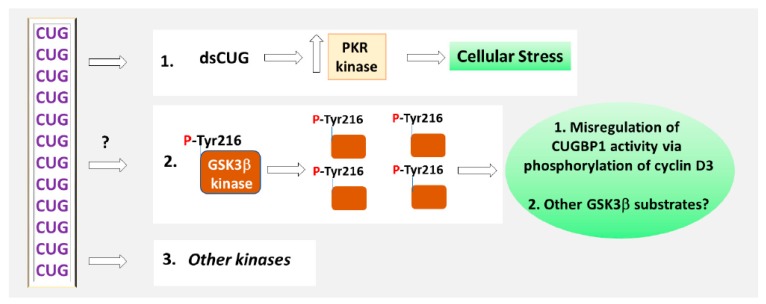
Figure 3.
Disruption of the signaling pathways in DM1. The mutant CUG repeats increase PKR kinase, which causes cellular stress in DM1. The toxic CUG-containing RNA increases phosphorylation of GSK3β at Tyr-216. As the result, GSK3β stability is increased in DM1. The elevation of active GSK3β in DM1 cells causes misregulation of CUGBP1 activity via phosphorylation and degradation of one of the substrates of GSK3β, cyclin D3. The alterations of other substrates of GSK3β in DM1 remain to be studied. The mechanism by which the mutant CUG repeats increase phosphorylation of GSK3β at Tyr-216 is unknown. Other kinases might be misregulated by the mutant CUG repeats in DM1 directly and via indirect pathways.