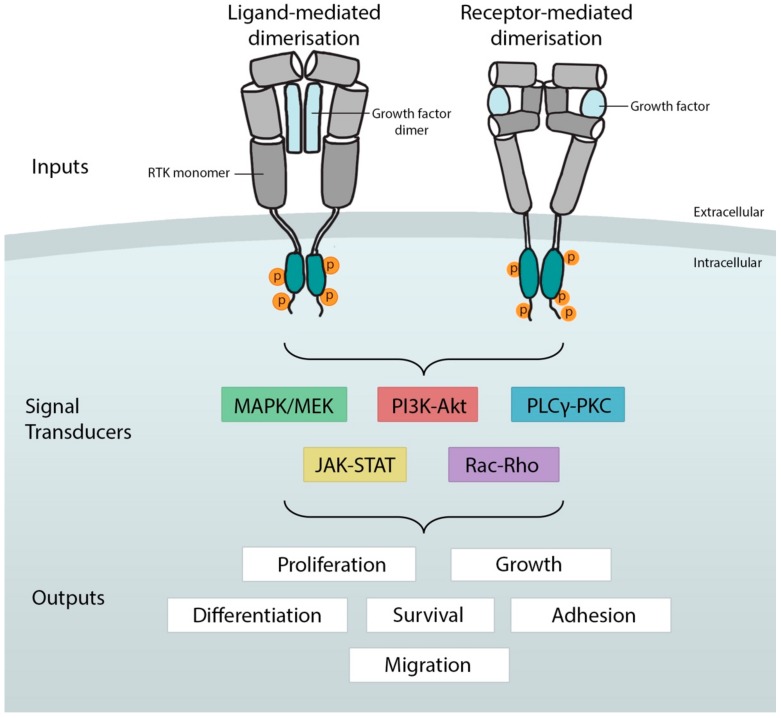
Figure 1.
General overview of receptor tyrosine kinase activation, signaling, and the cell-fate decisions they influence. The binding of growth factors (inputs) in the extracellular milieu induces conformation changes in the receptor monomer that enables dimerization. Enzymatic autophosphorylation (circled p) by intracellular tyrosine kinase domains in trans results in recruitment of one or more signal transduction cascades. These relay the signal to effectors that determine cell fates (outputs). Mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–protein kinase B, PI3K–Akt; phospholipase C gamma–protein kinase C, PLCgamma–PKC; Janus kinase and signal transducer and activator of transcription, JAK–STAT.