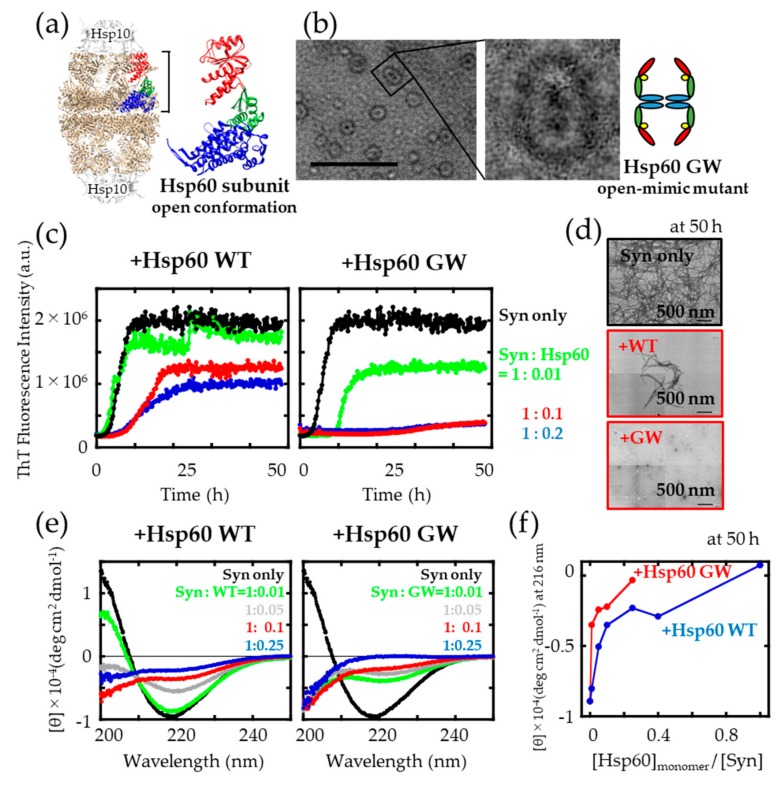
Figure 1.
Influence of Hsp60 wild type (WT) and GW on α-synuclein aggregation. (a) The open conformation of Hsp60 (PDB ID: 4PJ1), using UCSF Chimera [32]. Left: overall side profile structure of PDB ID: 4PJ1. Right: Hsp60 subunit in the open conformation. Apical domain (red), intermediate domain (green), and equatorial domain (blue). (b) TEM observation and simplified side view of Hsp60 GW. Scale bar = 50 nm. (c) Time course of Thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence changes upon incubation of α-synuclein in the absence (black) and presence of a 0.01 (green), 0.1 (red) and 0.2 (blue) fold concentration (monomer: monomer) of Hsp60. (d) TEM images of α-synuclein samples shaken in either the absence or presence of a 0.1 monomer-molar ratio of Hsp60 (scale bar: 500 nm). (e) Circular dichroism (CD) spectra of α-synuclein samples recorded at 25 °C after agitation. The raw data were corrected for contributions of native Hsp60 by subtraction. (f) Hsp60 concentration-dependent changes in the CD absorbance signal at 216 nm.