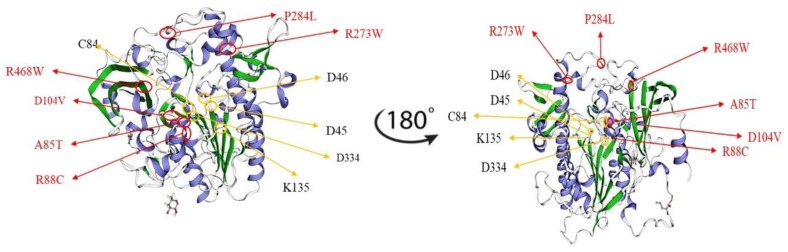
Figure 5.
3D structure analysis by simulating six missense residues, i.e., c.253G>A (p.A85T), c.262C>T (p.R88C), c.311A>T (p.D104V), c.817C>T (p.R273W), c.851C>T (p.P284L), and c.1402C>T (p.R468W), was performed using SWISS-MODEL. The location and the residues of A85T and P284L may have had less influence on the structure of IDS protein and its function and were considered to cause the attenuated phenotype. The altered residues that may have strongly influenced the confirmation of the active site on IDS protein were identified by 3D structure analysis, i.e., R88C, D104V, R273W, and D104V variants may have been pathogenic variations for the severe phenotype of Hunter syndrome.