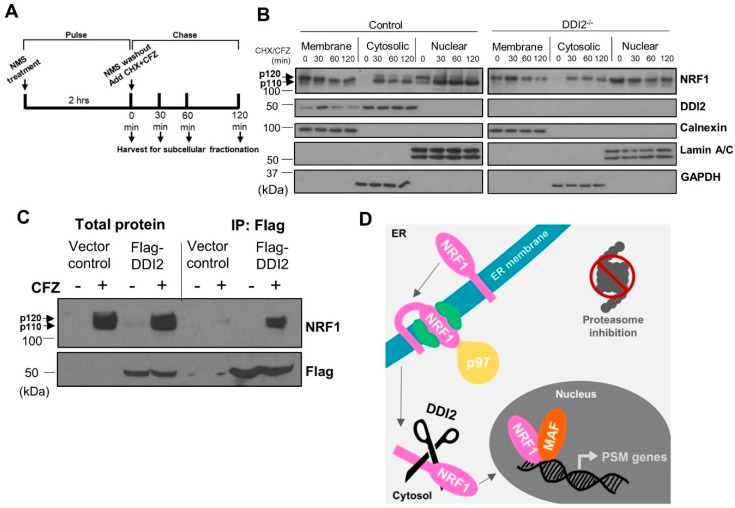
Figure 2.
DDI2-mediated proteolytic processing of NRF1 occurs in the cytosol. (A) Schematic representation of the pulse-chase assay is shown. (B) NIH-3T3 control (wild-type) and DDI2−/− cells were pulsed with 10 μM NMS-873 (p97 inhibitor) for 2 h, then chased with 50 μg/mL cycloheximide (CHX) and CFZ (5 μM) for 0, 30, 60, or 120 min. Subcellular fractionation of membrane-bound, cytosolic, and nuclear proteins was analyzed by western blot using the antibodies indicated. Calnexin, Lamin A/C, and GAPDH are fractionation controls for membrane-bound, nuclear, and cytosolic proteins, respectively. Blots shown are representative of three independent experiments. (C) MDA-MB-231 cells stably expressing Flag-DDI2 or a vector control were treated with 200 nM carfilzomib (CFZ) or equal volume DMSO for 4 h. The lysates derived from these cells were then subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag affinity gel. Input and immunoprecipitated proteins were probed for by western blot using the indicated antibodies. Blots shown are representative of three independent experiments. (D) A proposed model of NRF1 activation by DDI2 is shown. When the proteasome is inhibited, NRF1 is extracted out of the ER membrane via the action of ATPase p97 into the cytosol. NRF1 is then cleaved by DDI2 before it translocates into the nucleus as an active transcription factor.