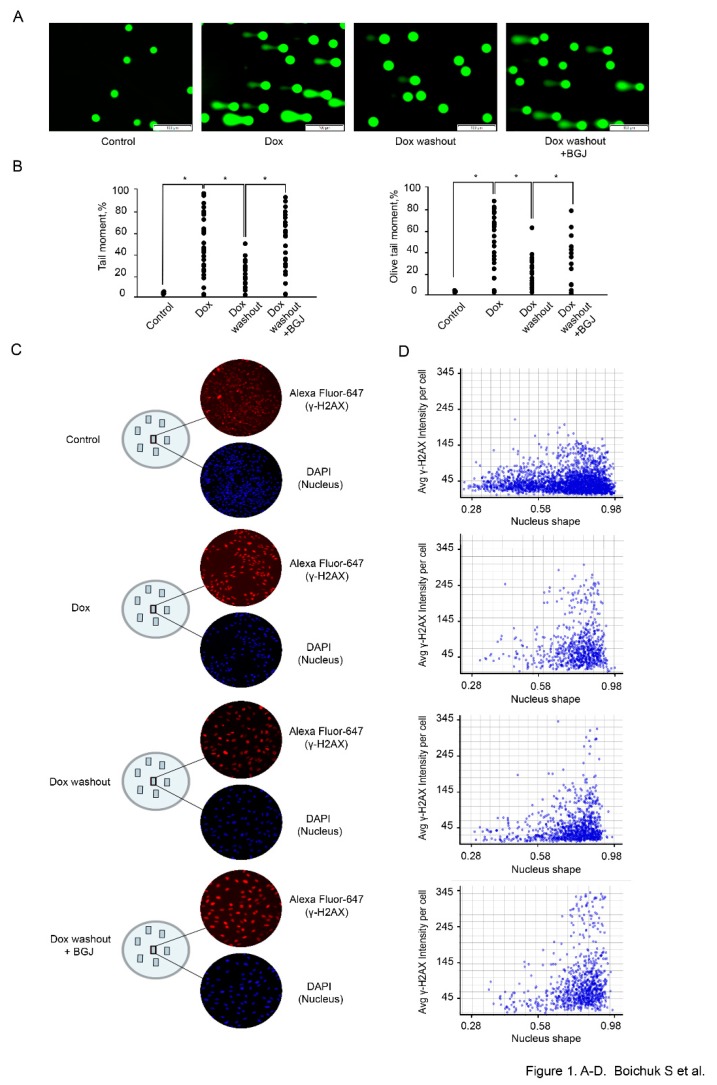
Figure 1.
Inhibition of FGF-signaling delays the kinetics of γ-H2AX decline in doxorubicin-treated GIST cells. GIST T-1 cells treated with solvent (control) and doxorubicin (dox) 0.5 μg/mL for 2 h following washout for 8 h and culture in the absence (Dox washout) and presence of BGJ398 (1 µM), an FGFR1-4 inhibitor (Dox washout + BGJ398). (A) Representative images of comets from theWe added experimental settings indicated above (Scale bars = 100 μm). (B) Graphic depiction of the calculated Tail Moment and Olive Tail Moment from analysis of alkaline Comet Assay shown in Figure 1A. Data is shown for a representative experiment, where at least 50 comets were quantitated for each experimental condition. (C) Cells were grown on slides for 24 h and treated with Dox and BGJ398 as indicated above. Cells were fixed and stained with DAPI (blue) and γH2AX-specific antibody (red). γH2AX-specific fluorescence intensity was measured for each nucleus (DAPI) and quantified automatically. (D) Histograms of γ-H2AX-specific fluorescence at the single-nucleus level. All images were acquired by GE Cytell imager as described in “Materials and methods”.