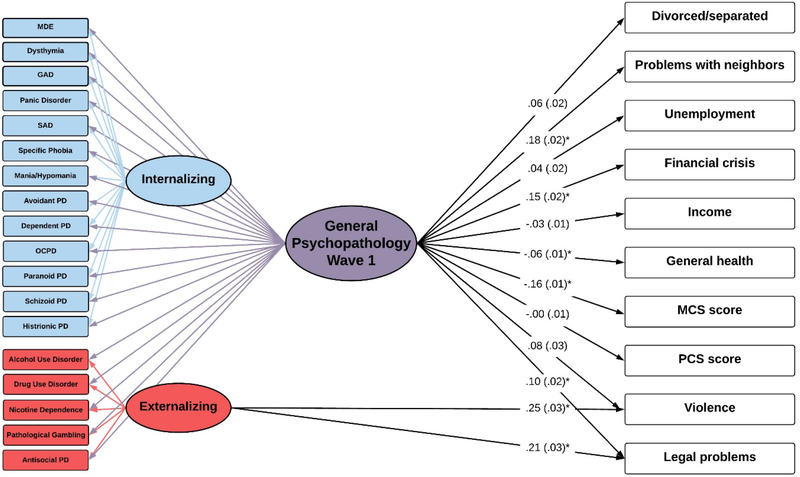
Figure 1. Bifactor model with one internalizing and one externalizing factors testing the shared and specific effects of past-year Axis I disorders and lifetime personality disorders (assessed in Wave 1) on the occurrence of adverse outcomes in Wave 2 of the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (N=34653).
Ellipses are used to denote latent constructs, rectangles are used to denote the observed variables measuring or impacting on these constructs. The bifactor model parses disorder variance into general variance (i.e., variance of the general psychopathology factor), variance of dimensions of psychopathology (e.g., variance of the externalizing dimension) and unique variance (variance of each mental disorder per se). Regression coefficients shown are standardized. Values in brackets indicate their standard errors. * indicate significant effects (two-sided p<0.05/210, i.e., p<0.00024). All results are adjusted for sociodemographic characteristics (sex, age and race/ethnicity) and each adverse outcome at Wave 1. Abbreviations: MDE, major depressive episode; GAD, generalized anxiety disorder; SAD, social anxiety disorder; OCPD, obsessive-compulsive personality disorder; PD, personality disorder; MCS, Mental Component Summary Score; PCS, Physical Component Summary Score. The Wave 1 outcomes (e.g. divorced/separated, problems with neighbors at Wave 1) were included as direct effects to each of the respective W2 outcomes and were allowed to freely correlate with one another at Wave 1 (arrows not shown). The Wave 2 outcomes were also allowed to freely correlate with one another (arrows not shown).