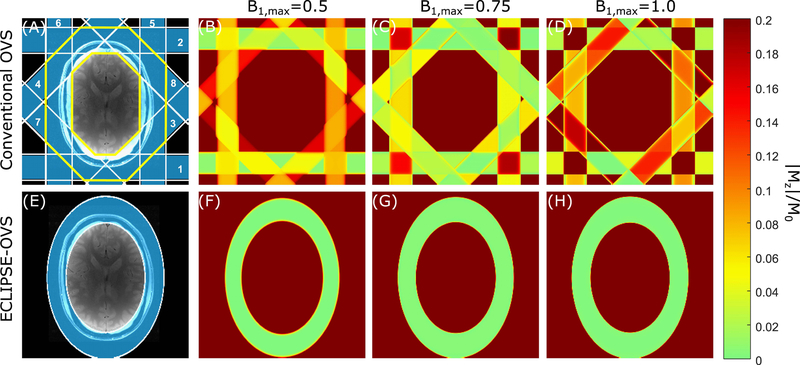
FIG. 1.
Comparison of conventional-OVS and ECLIPSE-OVS methods. (A, E) ROI placement for the conventional-OVS and ECLIPSE-OVS methods, respectively, which are overlaid on an axial brain slice. (A) The conventional-OVS method was implemented with 30mm thick slices at fixed 45° increments and two cycles placed around the scalp. The order in which slices were played out is marked. The extracranial ROI considered in optimizations is marked by the yellow boundary. (B, C, D) illustrate spatially differential relaxation of lipid resonances (T1=380 ms) due to non-instantaneous OVS pulses, and regions that experience/do not experience overlapping slices, for B1,max = 0.5, B1,max = 0.75, and B1,max = 1.0, corresponding to a − 33.33%, 0%, and + 33.33% variation in B1, respectively. (F, G, H) illustrate lipid suppression (< 0.02) with ECLIPSE-OVS, where no differential relaxation of lipid resonances is seen due to single-shot outer volume selection, while being insensitive to ± 33.33% B1 variation.