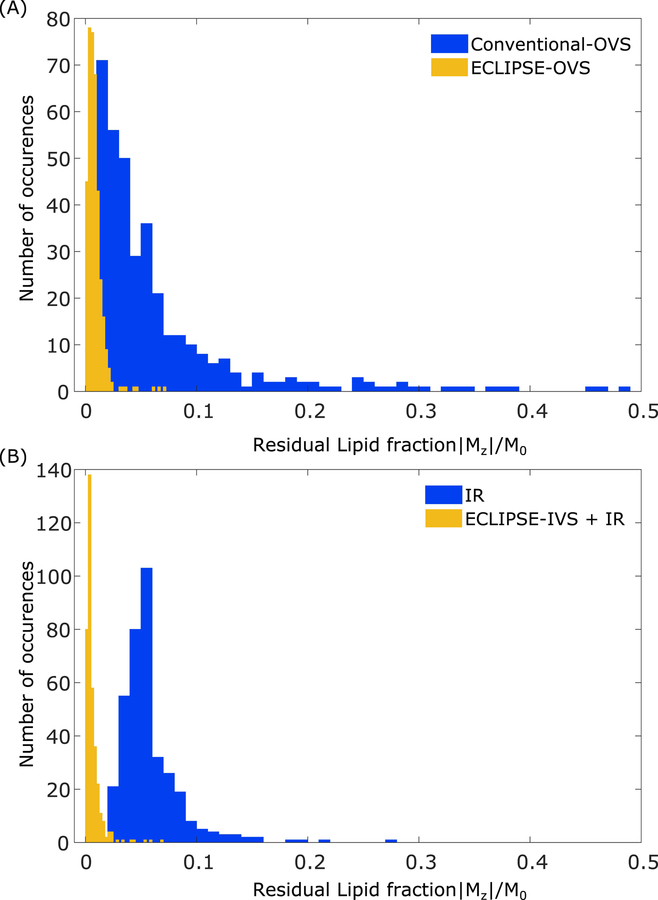
FIG. 6.
Residual lipid magnetization for conventional-OVS, ECLIPSE-OVS, IR, and ECLIPSE-IVS + IR sequences. Each histogram contains the combined data from all three volunteers, amounting to 375 and 370 voxels for OVS and IR-based methods, respectively. (A) The residual lipid fractions for the conventional-OVS sequence appear consistent with observations in Figure 4, and most voxels have sufficient suppression (|Mz|/M0 < 0.075), with ~10% of the voxels with |Mz|/M0 > 0.1 that span as high as ~0.48. Lipid suppression with ECLIPSE-OVS in comparison, is seen to be robust and highly effective, with 96% of the voxels with |Mz|/M0 < 0.02. The highest residual lipid fraction observed with ECLIPSE-OVS across all volunteers is 0.071. (B) The spread of residual lipid fraction with the IR sequence is less than the conventional-OVS method, with 6.5% of the voxels with |Mz|/M0 > 0.1. Lipid suppression performance of the ECLIPSE-IVS + IR sequence is similarly robust to ECLIPSE-OVS, with ~94% of the voxels with (|Mz|/M0 < 0.015). The highest lipid fraction observed with ECLIPSE-IVS + IR is 0.068.