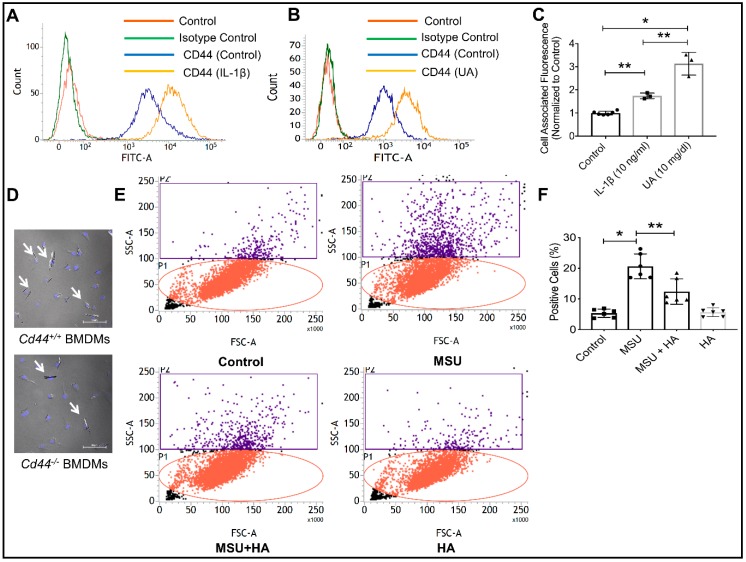
Figure 1.
The CD44 receptor is highly expressed on differentiated human THP-1 macrophages, is induced by proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and soluble uric acid (UA) and is directly involved in the phagocytosis of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals. * p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01. Data are presented as scatter plots of 3–5 independent experiments with mean and standard deviations highlighted. (A) A representative flow cytometry plot showing the expression of CD44 receptor on THP-1 macrophages and the impact of IL-1β (10 ng/mL) treatment on CD44 receptor protein expression. A rightward shift was observed indicative of increased receptor density on cell surface. (B) A representative flow cytometry plot showing enhanced CD44 receptor localization on THP-1 macrophages following treatment with UA (10 mg/mL). (C) CD44 receptor staining was significantly higher in IL-1β and UA-treated macrophages compared to untreated cells. (D) MSU crystals were detected intracellularly to a greater extent in bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) from CD44 competent animals (Cd44+/+) compared to BMDMs from CD44 knockout animals (Cd44−/−). (E) Representative flow cytometry plots depicting increased cell side-scatter of THP-1 macrophages as a result of MSU phagocytosis. Treatment with the CD44 receptor-ligand hyaluronic acid (HA; 100 μg/mL) reduced MSU phagocytosis indicated by a reduction in macrophage cell side scatter. (F) HA treatment significantly reduced MSU phagocytosis by THP-1 macrophages.