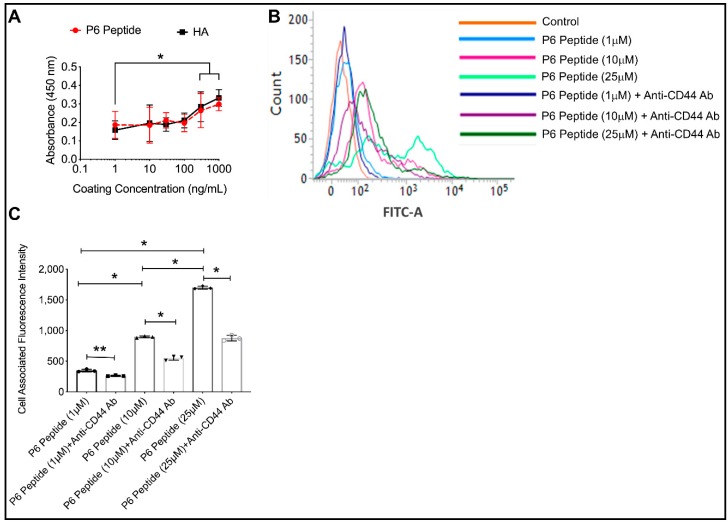
Figure 2.
Comparative binding of the P6 peptide and high molecular weight hyaluronic acid (HA) to the recombinant human CD44 receptor using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) format and CD44-dependent association of fluorescein-P6 peptide with human THP-1 macrophages. Fluorescein-P6 peptide was incubated with THP-1 macrophages for 60 min in the absence or presence of an anti-CD44 antibody (Ab; 2.5μg/mL) and cell-associated fluorescence was determined by flow cytometry. Data are presented as the mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments. * p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01. (A) The P6 peptide and HA exhibited a concentration-dependent binding to the CD44 receptor with no difference in binding signals between the P6 peptide and HA across all coating concentrations. (B) A representative flow cytometry plot showing reduced association of the P6 peptide with THP-1 macrophages in the presence of an anti-CD44 Ab. (C) Neutralization of the CD44 receptor significantly reduced the P6 peptide association with THP-1 macrophages.