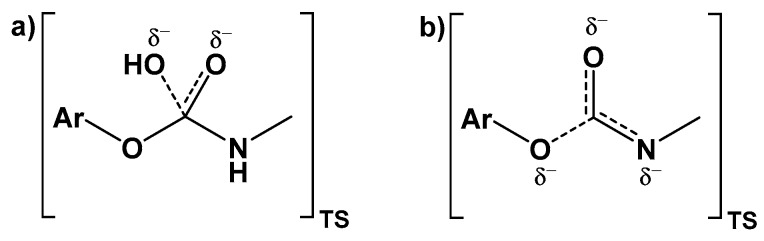
Figure 8.
Proposed transition states on two possible reaction pathways for hydrolysis of an aryl carbamate ester: (a) via an energetically less favoured addition-elimination (BAc2) mechanism, or (b) via the energetically more favoured elimination-addition (E1cB) mechanism. The latter mechanism is not possible for carbamate esters lacking an N-H group.