Figure 2. DoubletDecon Readily Distinguishes Experimentally Validated Doublets in Species-Mixing scRNA-Seq.
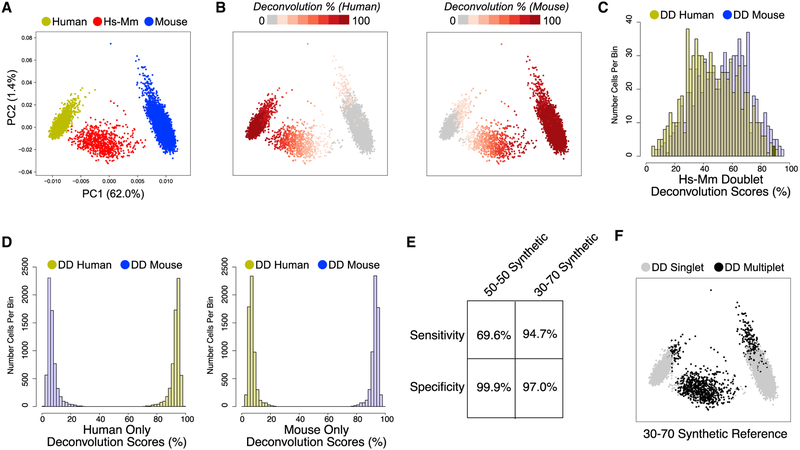
(A) Separation of mouse, human, and mixed-species doublet scRNA-seq profiles by principal-component analysis (PCA) of ICGS variable genes. Species assignments are defined by the total number of aligned reads to either human (yellow), mouse (blue), or both (red) genomes.
(B) Projection of species-specific deconvolution results (against human or mouse ICGS clusters) are displayed along the same PCA plot. Cells in gray indicate <10% identify to the indicated cluster, >90% in dark red, and lighter shades of red indicating intermediate scores.
(C) Histogram of the mouse (blue) and human (yellow) DCP results (x axis) for known species mixed cells, indicating a bi-modal distribution for deconvolution scores peaking at 30% and 70%.
(D) The same histogram is shown for deconvolution scores in only human cells (left) and only mouse cells (right), indicating a skewed distribution toward the correct species.
(E) The accuracy of DoubletDecon doublet predictions using synthetic reference doublets derived from either a 50/50 equal contribution of cell transcriptomes (“only50” parameter) or from weighted averages of 30/70 and 70/30, in addition to the 50/50 synthetic doublets.
(F) Projection of final called doublets (black) in the PCA, using 30/70 synthetic doublets.