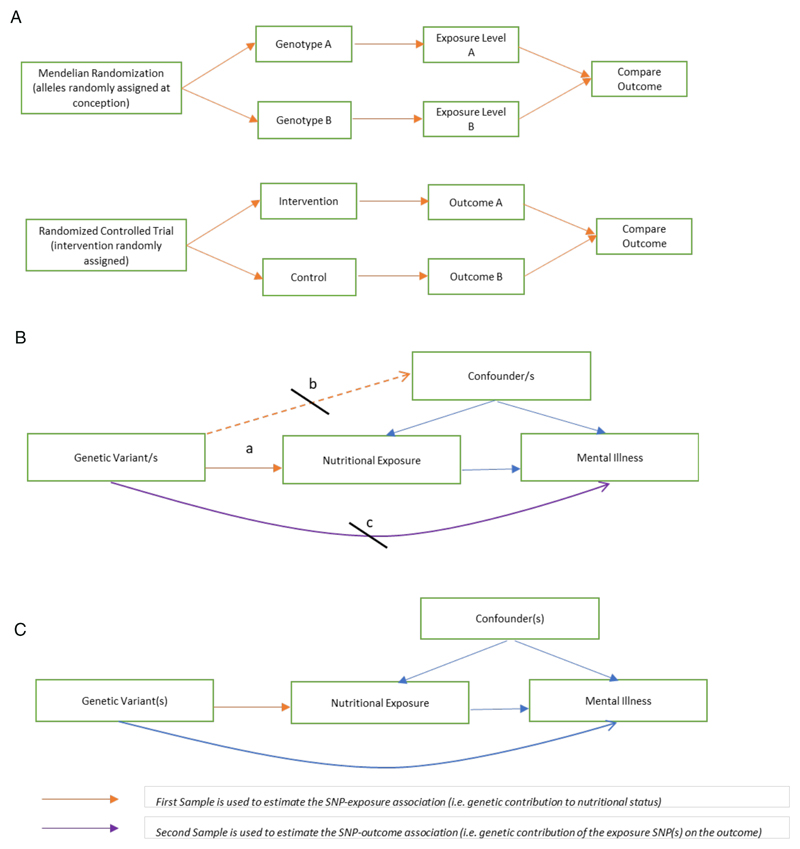
Figure 1. Mendelian Randomization: comparisons and assumption.
1a Mendelian Randomization as a ‘natural’ Randomized Controlled Trial
MR has been compared to a randomized controlled trial, with random allocation of genetic alleles at conception could be considered analogous to random allocation of interventions in a trial.
1b Assumptions in Mendelian Randomization
MR assumes that the genetic variants are: a. associated with the exposure of interest; b. not associated with confounders; and c. only associated with the outcome through the exposure
1c Two-sample Mendelian Randomization
Two-sample MR takes estimates of the SNP-exposure association from one population (e.g. a nutritional exposure GWAS) and the SNP-outcomes association from a separate sample (e.g. a psychiatric outcome GWAS).