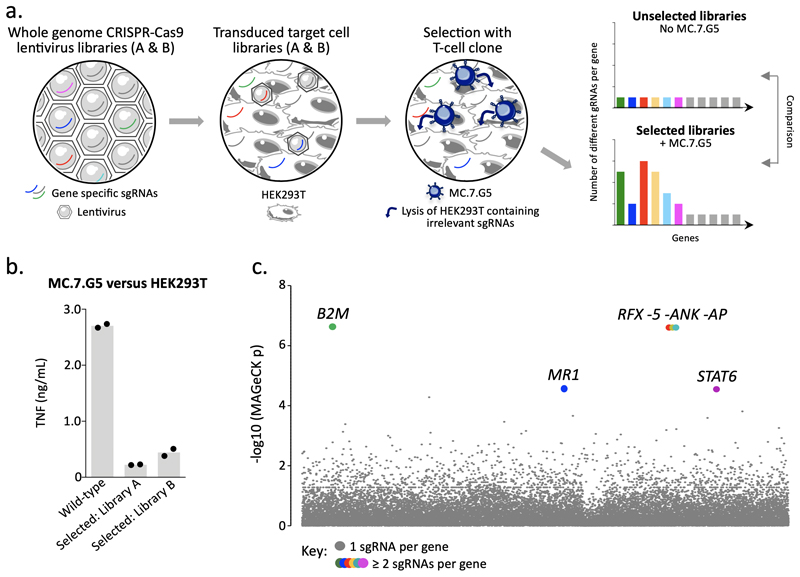
Figure 2. Whole genome CRISPR-Cas9 library screening reveals MR1 as the candidate target of MC.7.G5.
(a) Overview of the approach used to reveal the ligand of MC.7.G5. GeCKO v2 whole genome CRISPR-Cas9 libraries A and B were used as lentivirus to transduce target cell line HEK293T. MC.7.G5 lysed HEK293T expressing sgRNAs for genes that are irrelevant for HEK293T recognition, thereby enriching sgRNAs for genes that are essential for cancer cell lysis by MC.7.G5. Two rounds of selection with MC.7.G5 were performed and comparison of selected libraries unselected HEK293T (no MC.7.G5) revealed enriched sgRNAs. (b) MC.7.G5 recognition of selected HEK293T library post-selection is greatly reduced compared to wild-type HEK293T, suggesting key genes had been ablated by the whole genome CRISPR-Cas9 approach. Overnight activation and TNF ELISA, performed in duplicate. Bars depict the mean. (c) MR1 was identified as one of key genes for MC.7.G5 recognition of HEK293T. Total genomic DNA from 3 x107 selected and unselected HEK293T libraries was used for sequencing, followed by MAGeCK analysis. Highlighted (coloured) genes with y genes for MC.7.G5 recognition of HEK293T.reduced