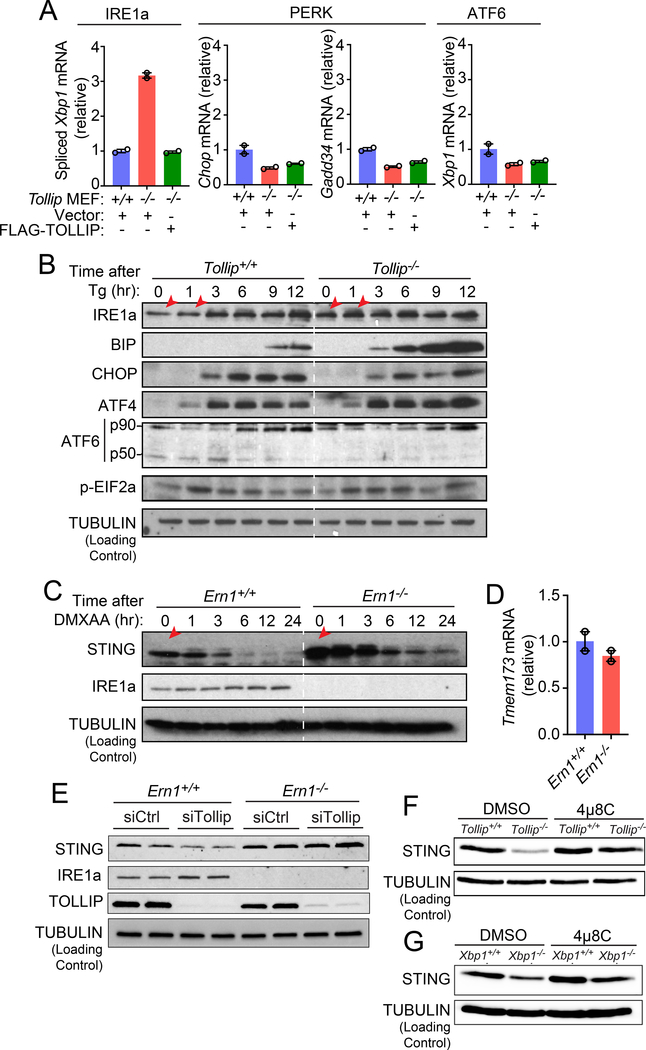
Figure 6: Tollip-deficiency selectively activates IRE1α, which facilitate resting-state STING protein turnover.
(A) qRT-PCR analysis of basal expression of UPR genes in Tollip+/+ and Tollip−/− MEFs stably expressing an empty vector or Flag-TOLLIP. A representative experiment with 2 biological replicates is showing. Experiments were repeated three times.
(B) Immunoblot analysis of UPR proteins in Tollip+/+ and Tollip−/− MEFs treated with thapsigargin (Tg, 500 nM) for indicated amount of time (top). Red arrows denote increased IRE1α in Tollip−/− MEFs.
(C) Immunoblot analysis of Ern1+/+ and Ern1−/− MEFs stimulated with DMXAA (10 μg/ml) for indicated amount of time (top).
(D) qRT-PCR analysis of basal Tmem173 mRNA in Ern1+/+ and Ern1α−/− MEFs. A representative experiment with 2 biological replicates is showing. Experiments were repeated three times.
(E) Immunoblot analysis of Ern1+/+ and Ern1−/− MEFs after treatment with control siRNA or siTollip.
(F) Immunoblot analysis of Tollip+/+ and Tollip−/− MEFs treated with DMSO or IRE1α inhibitor 4μ8C (100 μM) overnight.
(G) Immunoblot analysis of Xbp1+/+ and Xbp1−/− MEFs treated with DMSO or 4μ8C (100 μM) overnight. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.