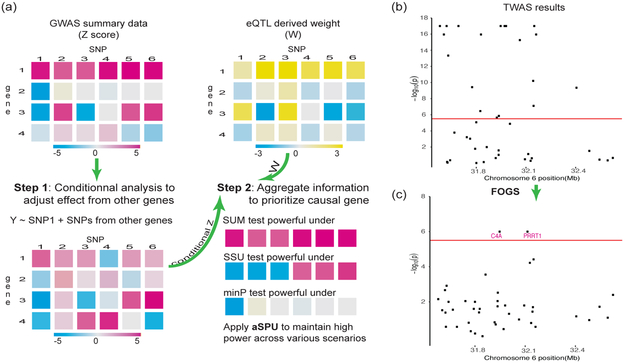
Figure 1: Overview of the fine-mapping method: FOGS.
a. FOGS prioritizes causal genes by two steps: first, FOGS conducts a conditional analysis with ridge regression to account the effects of other SNPs/genes in the locus; second, FOGS integrates eQTL-derived weights and conditional Z scores by an adaptive test to maintain high power. b and c, TWAS and FOGS were performed on summary statistics from a schizophrenia GWAS of 105,318 European individuals [27]. b, TWAS results for a locus on chromosome 6 (31.6–32.7 Mb). c, FOGS results for the same locus on chromosome 6 (31.6–32.7 Mb). 19 out of 42 genes in the locus has been identified to be significant by TWAS, prompting for fine-mapping. FOGS prioritized putative causal genes by successfully identifying the well-known schizophrenia-related gene C4A [33].