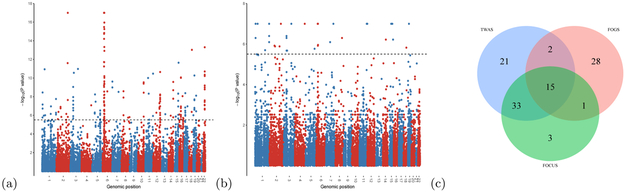
Figure 5: Applications to a GWAS schizophrenia summary data [27].
a, Manhattan plot of all TWAS associations. b, Manhattan plot of FOGS results (see Methods). For a and b, each point represents a single gene tested, with physical position (P0) plotted on the x axis and −log(p) values plotted on the y axis. Dashed lines indicate genome-wide significant threshold (0.05/16,000 ≈ 3.1 × 10−6). c, Venn diagram of the putative causal genes prioritized by different methods for the risk regions that contained at least two genes. TWAS stands for the results of selecting the most significant gene in each region plus the genes with p-value < 1e − 17 (unable to distinguish) as putative causal genes. FOGS and FOCUS represent the results of FOGS with a stringent cutoff (0.05/16,000 ≈ 3.1 × 10−6) and FOCUS with 90% credible gene-sets, respectively (see Methods).