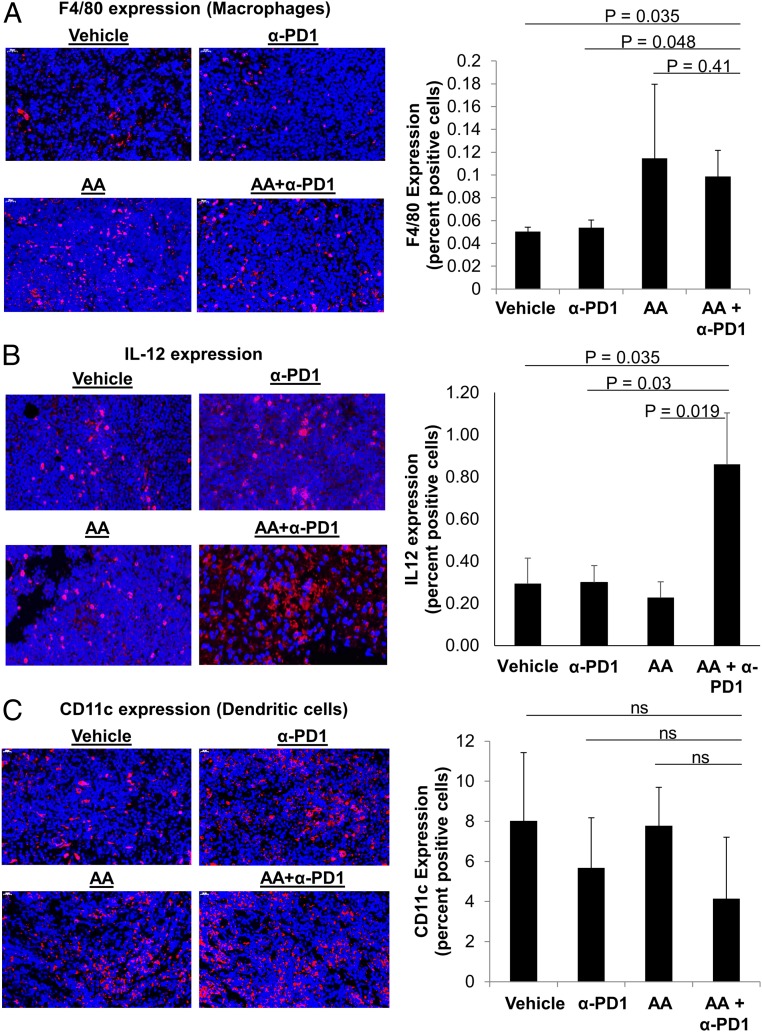
Fig. 6.
High-dose AA and anti-PD1 treatment combination leads to increase in tumor macrophage infiltration and IL-12 production but does not change dendritic cell infiltration. (A) The mouse macrophage marker, F4/80, was increased in mice receiving AA either as a single agent or combination. The percent of intratumoral macrophages was higher in AA+α-PD1 compared to vehicle (P = 0.035) and α-PD1 alone (P = 0.048). See also SI Appendix, Fig. S6. (B) IL-12 (a cytokine produced by activated APCs and in turn activates cytotoxic T cells and NK cells) was significantly increased in the AA+ α-PD1 group compared to α-PD1 alone (P = 0.03), AA alone (P = 0.019), and vehicle (P = 0.035). (C) CD11c (dendritic cell) expression was not significantly different between treatment groups (ANOVA, P > 0.1). See also SI Appendix, Fig. S7. Data expressed as means ± SEM of 5 representative mouse tumors per treatment group; all tumors were harvested on day 19 (day 9 after treatment initiation). Immunofluorescence images were captured at 50× magnification, as indicated. ns, not significant. Immunofluorescence staining was quantified by artificial intelligence technology.