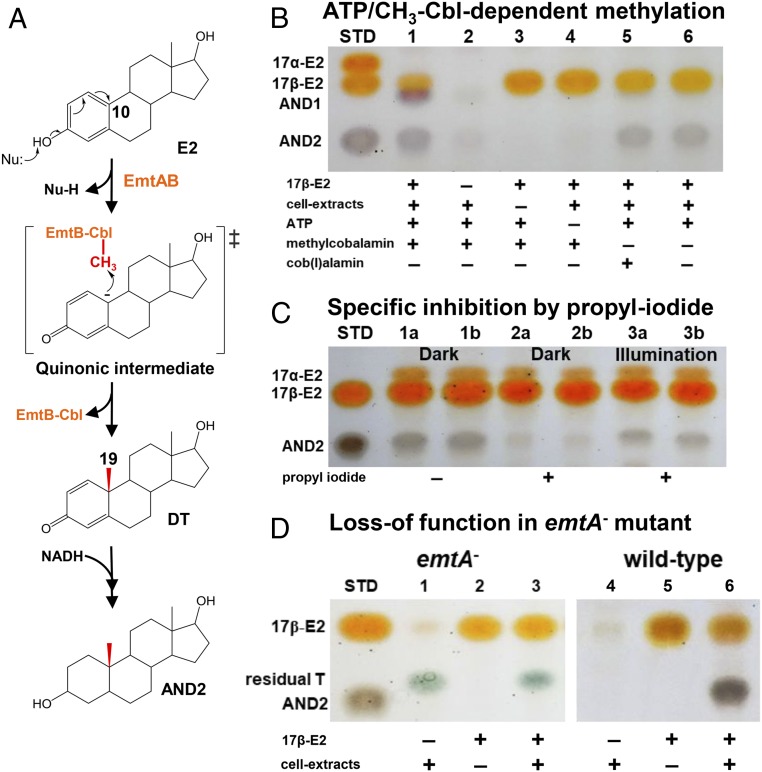
Fig. 7.
Proposed mechanism for the Emt-catalyzed, cobalamin-mediated estradiol methylation. (A) Proposed mechanism involved in estrogenic A-ring activation and subsequent cobalamin-mediated C-10 methylation to form androgens. (B–D) TLC analysis of the cobalamin-mediated estradiol methylation in the strain DHT3 cell extracts. (B) ATP (lane 4) and methylcobalamin (lanes 5 and 6) are required for the estradiol (E2) methylation. (C) Specific inhibition of the E2 methylation in the strain DHT3 cell extracts by propyl iodide (lanes 2a/2b) in a reversible manner with daylight (lanes 3a/3b). Assays a and b are technical replicates in each treatment. All assays in C contain E2, cell extracts, ATP, NADH, and with or without propyl iodide. (D) Loss of E2 methylation activity in the cell extracts of the emtA-disrupted strain DHT3 mutant (lane 3). Assays 3 and 6 in D contain E2, cell extracts, ATP, NADH, and methylcobalamin. Abbreviations: AND1, 17β-hydroxyandrostan-3-one; AND2, 3β,17β-dihydroxyandrostane; DT, 1-dehydrotestosterone; Nu, nucleophile; STD, steroidal standards; and T, testosterone.