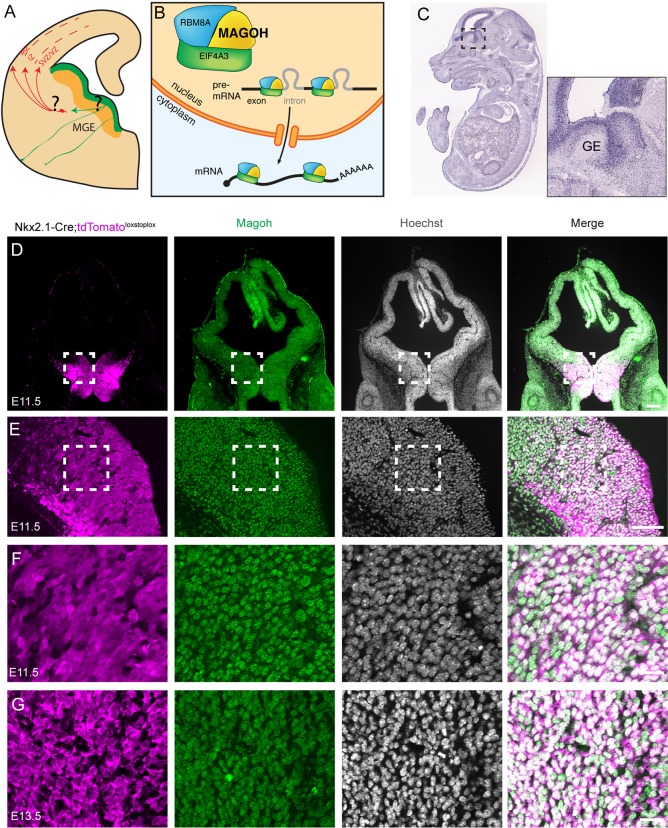
Fig. 1.
Magoh is expressed within germinal zones of the mouse embryonic ganglionic eminence. (A) Schematic of embryonic interneuron development depicting the medial ganglionic eminence (MGE), where progenitors (green) produce interneurons (red), which then migrate into the cortex. This study investigates requirements for Magoh in cellular processes demarcated by questions marks. (B) Schematic of the exon junction complex (EJC) bound to pre-mRNA and mRNA in the nucleus and cytoplasm, respectively. (C) Magoh in situ hybridization of an E14.5 embryo with boxed region (right) depicting robust expression in progenitor zones of the ganglionic eminences (GE). (D-F) Coronal sections of E11.5 Nkx2.1-Cre;RosaloxSTOPloxtdTomato brains co-immunostained for Magoh (green), RFP (tdTomato, magenta) and Hoechst DNA stain (white). The boxed areas in D and E are magnified in E and F, respectively. (G) High-magnification images of E13.5 MGE co-stained as in F. Scale bars: 200 µm (D); 50 µm (E); 25 µm (F,G).