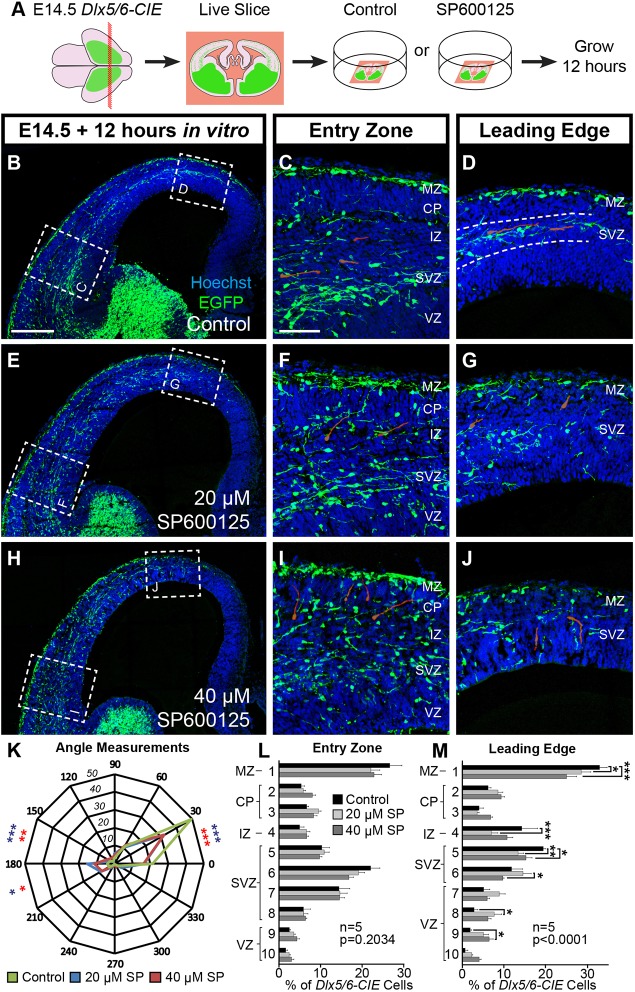
Fig. 1.
JNK activity is required for cortical interneurons to remain tangentially oriented in migratory streams. (A) Schematic diagram illustrating ex vivo slice culture of E14.5 Dlx5/6-CIE brains in control or SP600125-treated conditions. (B-D) In control slices, cortical interneurons travel tangentially in migratory streams in the MZ and SVZ (dashed lines, D). (E-J) Streams are disrupted with 20 μM (E-G) and 40 μM (H-J) SP600125. Representative interneurons are highlighted in red. (K) Quantification of leading process angles. Interneurons are more tangentially oriented in control (200 cells) compared with 20 µM (178 cells; P=0.0009) and 40 µM (256 cells; P=0.0014) SP600125 conditions (χ2 test). (L,M) Interneurons in JNK-inhibited conditions are significantly displaced at the leading edge (two-way ANOVA: F(18,120)=3.582; P<0.0001). All analyses were performed on n=5 brains/condition from at least four experimental days. Data are mean±s.e.m. ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05, Fisher's LSD post-hoc test. Scale bars: 250 μm in B,E,H; 75 μm in C,D,F,G,I,J.