Figure 5.
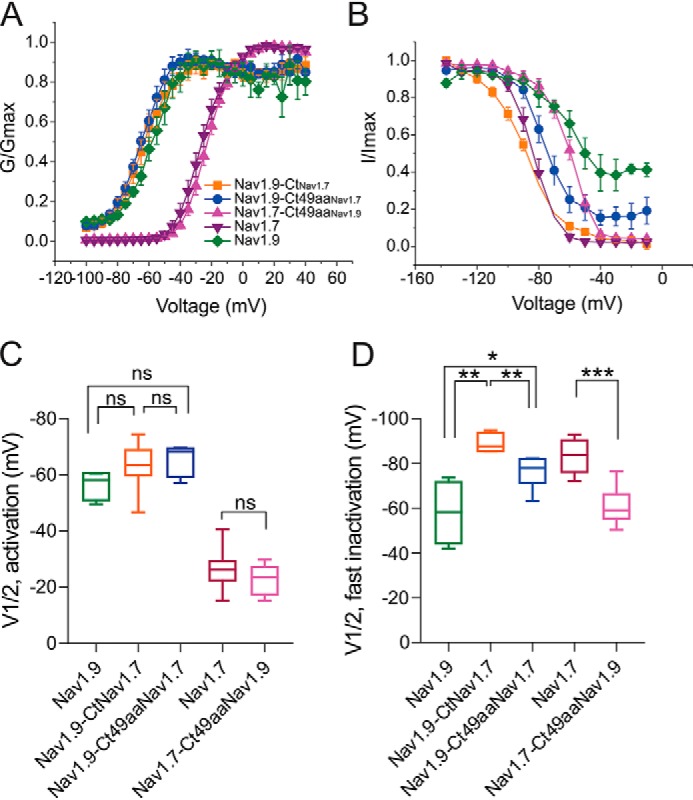
The C terminus of Nav1.9 modulates voltage-dependence of steady-state fast-inactivation but not activation. Boltzmann fits of voltage dependence of activation (A) and steady-state fast inactivation (B) for WT Nav1.9 and Nav1.7 channels and their chimeras. C, comparison of midpoint voltage of activation (V½Act) among all tested channels showing no difference in chimeric channels Nav1.9-CtNav1.7 (n = 8), Nav1.9-Ct49aaNav1.7 (n = 7), and Nav1.7-Ct49aaNav1.9 (n = 10), compared with parent channels Nav1.9 (n = 4) and Nav1.7 (n = 10). D, comparison of midpoint voltage of fast inactivation (V½Inact) among all tested channels (Nav1.9-CtNav1.7 (n = 8); Nav1.9-Ct49aaNav1.7 (n = 7); Nav1.7-Ct49aaNav1.9 (n = 10); Nav1.9 (n = 4); Nav1.7 (n = 10)). Error bars, S.E. Statistical significance is indicated by asterisks: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001, by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple-comparison test. ns, not significant.
