Figure 3.
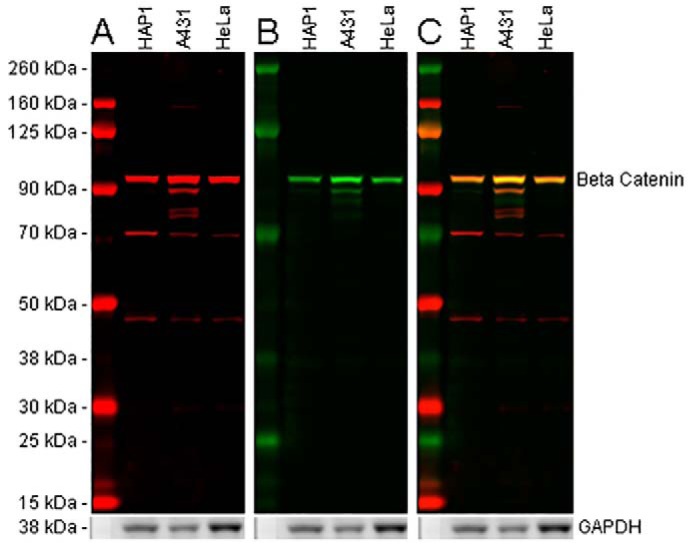
Multiple epitope approach to detect β-catenin in cell lysates and to identify potential off-target antibody binding. 20 μg of HAP1, A431, and HeLa lysates were loaded into a 4–12% BisTris gel and run under the MOPS buffer system. The membrane was blocked for 1 h using Odyssey blocking buffer (TBS) before incubation with mouse anti-β-catenin antibody (ab231305) (A) and rabbit anti-β-catenin antibody (ab35272) (B) and at a 1 μg/ml concentration and 1:5000 dilution (0.0000126 μg/ml), respectively. Antibody binding was detected using goat anti-rabbit IgG H&L (IRDye® 800CW) preadsorbed and goat anti-mouse IgG H&L (IRDye® 680RD) preadsorbed secondary antibodies at 1:20,000 dilution for 1 h at room temperature. A, ab231305, binding to the C terminus and visualized in the 700-nm channel (red), displays a strong band at 95 kDa. However, there are several bands at a lower molecular weight present in all lysates. B, ab32572, binding the N terminus of β-catenin and visualized in the 800-nm channel (green), displays a single band at 95 kDa with an additional faint band at 90 kDa in A431 lysate only. C, when both 800- and 700-nm channels are displayed, both ab32572 and ab231305 show a band at 95 kDa, identifying the full-length β-catenin protein. The additional bands seen for ab231305 are not clearly shown to overlay with ab32572. This could represent off-target binding or isoforms lacking the N-terminal binding domain for ab32572. Membranes were visualized using the Odyssey CLx imager with auto-intensity and 84-μm resolution. The membrane was then probed with an anti-GAPDH rabbit antibody conjugated to HRP (ab9385). Staining was developed using a GBOX XT-16 chemiluminescent imager with a 20-min exposure.
