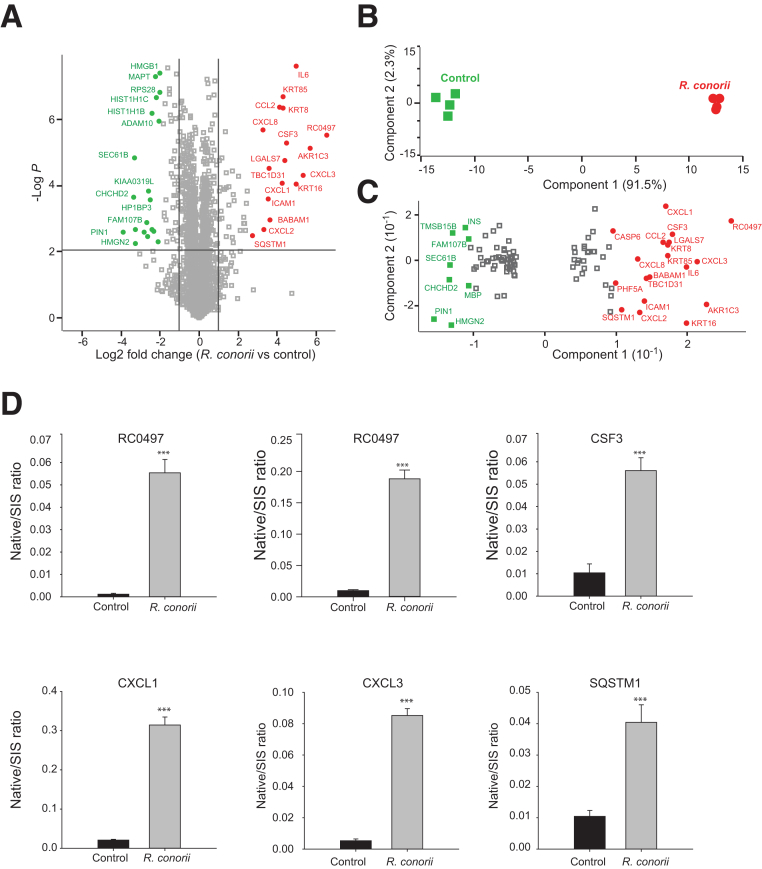
Figure 2.
Quantitative proteomics analysis of the secretome of primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) infected with Rickettsia conorii. The HUVECs were infected with R. conorii for 24 hours. The cell culture media were collected, and the secretory proteins from HUVECs were analyzed by label-free liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. A: Volcano plot of protein expression in the secretome of HUVECs infected with R. conorii. The dots above the horizontal line are proteins whose levels in the secretome of HUVECs were significantly changed in response to R. conorii infection (t-test; permutation-based FDR, 1%). Vertical lines indicate the twofold change cutoff. Some most significantly up-regulated or down-regulated proteins are labeled. B: Projection of principal component analysis of 104 proteins whose levels in the secretome of HUVECs were significantly changed in response to R. conorii infection (t-test with permutation-based FDR of 1% and twofold change cutoff). The first two components of data variability of 104 proteins, from four replicates of control HUVECs (green squares) and four replicates of R. conorii–infected HUVECs, are shown. C: Scatter plot depicts the protein feature loadings of component 1 and component 2 of the PCA in Figure 2B. Protein features showing significant importance in dividing control and rickettsial groups were labeled. D: Stable isotope dilution–selected reaction monitoring (SID-SRM)–MS validation of differentially expressed proteins. Five proteins that were up-regulated in the HUVEC secretome by R. conorii were selected for further validation with quantitative SID-SRM-MS. RC0497 was measured with two signature peptides. Error bars are the SEM of SRM measurements. ***P < 0.001 versus control (t-test). ADAM10, disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 10; AKR1C3, aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3; BABAM1, BRISC and BRCA1-A complex member 1; CCL2, C-C motif chemokine 2; CHCHD2, coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain-containing protein 2; CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; CXCL1, growth-regulated alpha protein; CXCL2, C-X-C motif chemokine 2; CXCL3, C-X-C motif chemokine 3; CXCL8, interleukin-8; FAM107B, protein FAM107B; HIST1H1B, histone H1.5; HIST1H1C, histone H1.2; HMGB1, high mobility group protein B1; HMGN2, non-histone chromosomal protein HMG-17; HP1BP3, heterochromatin protein 1-binding protein 3; ICAM1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IL6, interleukin-6; INS, insulin; KIAA0319L, dyslexia-associated protein KIAA0319-like protein; KRT16, keratin, type I cytoskeletal 16; KRT8, keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8; KRT85, keratin, type II cuticular Hb5; LGALS7, galectin-7; MAPT, microtubule-associated protein tau; MBP, myelin basic protein; PHF5A, PHD finger-like domain-containing protein 5A; PIN1, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1; RC0497, Putative N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase RC0497; RPS28, 40S ribosomal protein S28; SEC61B, protein transport protein Sec61 subunit beta; SIS, stable isotope labeled; SQSTM1, sequestosome-1; SQSTM1, sequestosome-1; TBC1D31, TBC1 domain family member 31; TMSB15B, thymosin beta-15B.