Figure 1.
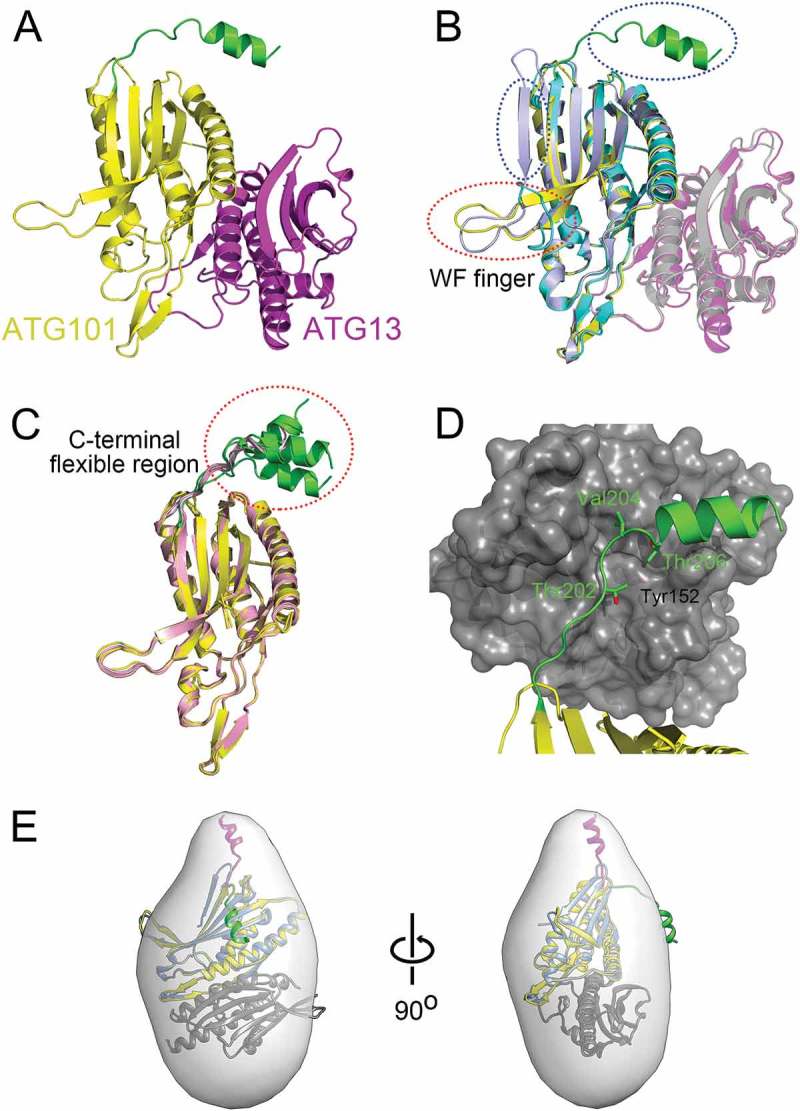
Structure of ATG101-ATG13HORMA complex. (a) Our HsATG101-ATG13HORMA complex showing the C-terminal helix of ATG101. ATG101 and ATG13HORMA are colored yellow and magenta, respectively. The unique C-terminal region of ATG101 is highlighted as green. (b) Superposition of HsATG101 structures showing clear differences in 2 regions, the WF-finger and the C-terminal region, which are highlighted by red and blue dotted circles, respectively. Our HsATG101-ATG13HORMA structure is colored as panel (A). The previous HsATG101-ATG13HORMA structure (C-terminal deleted version of HsATG101; PDB ID: 5C50) is colored slate and gray for ATG101 and ATG13, respectively. Free HsATG101 (β-sheet conformation of C-terminal region; PDB ID: 4WZG) is colored sky blue. (c) Superposition of all our structures of HsATG101 showing the flexibility of the C-terminal region. The HsATG101 with a helical C-terminal region is colored as panel (A) and that with random coil colored pink. (d) A close-up view of the interaction between the C-terminal region of HsATG101 and neighboring symmetry-equivalent ATG13 molecule shown in dark gray surface. The exposed aliphatic carbon atoms of Thr202, Val204, and Thr206 in ATG101 are stabilized by hydrophobic residues including Tyr152 in neighboring ATG13 in crystalline packing. (e) Our crystal structure of ATG101-ATG13HORMA and a modeled complex with the C-terminal β-sheet structure of ATG101 were fitted into the low-resolution molecular envelope generated from SAXS data. The C-terminal flexible α-helix of ATG101 colored green shows discrepancy for the SAXS molecular envelope and the simple rigid-body motion of the region colored magenta fits well into the SAXS envelope.
