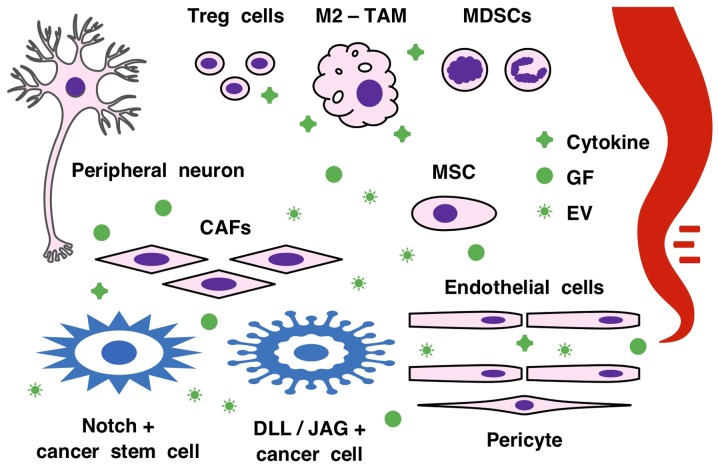
Figure 3.
Notch signaling network in the tumor microenvironment. CSCs, differentiated cancer cells, CAFs, endothelial cells, MSCs, pericytes, peripheral neurons and immune cells, such as TAMs, MDSCs and regulatory T (Treg) cells, constitute the tumor microenvironment. Cancerous and non-cancerous cells communicate via Notch ligand/receptor pairs for juxtacrine signaling, as well as via cytokines, GFs and EVs for paracrine signaling. Notch signaling cascades crosstalk with FGF and WNT signaling cascades in the tumor microenvironment to support the self-renewal of CSCs and regulate angiogenesis and immunity. The Notch signaling network exerts oncogenic and tumor-suppressive functions in a cancer stage- or (sub)type-dependent manner. CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; MSCs, mesenchymal stem/stromal cells; TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; EV, extracellular vesicle; GF, growth factor, MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; CSC, cancer stem cell; DLL, delta-like canonical Notch ligand; JAG, jagged canonical Notch ligand.