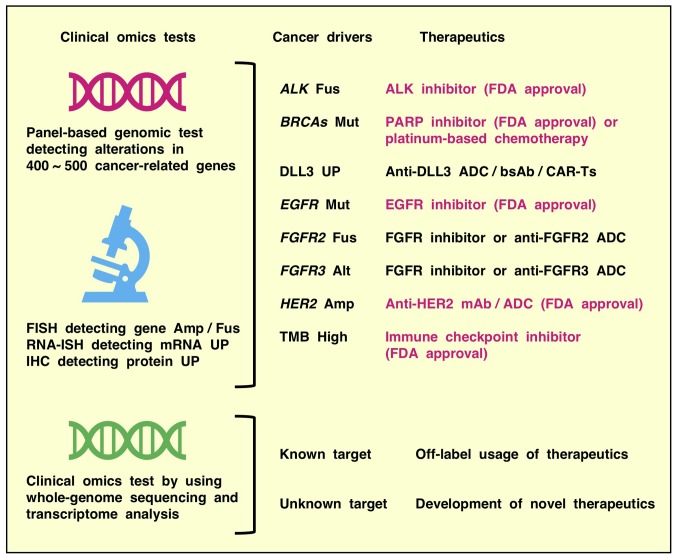
Figure 5.
Clinical omics tests for precision medicine. Panel-based genomic tests detecting mutations and other alterations in 400~500 cancer-related genes, FISH detecting gene Amp or Fus, RNA-ISH detecting mRNA upregulation and IHC detecting protein UP are utilized to match drugs to cancer patients in clinical oncology. Up-to-date panel-based genomic tests are reliably applied to detect biomarkers, such as cancer drivers and the TMB. By contrast, whole-genome sequencing and transcriptome analyses is applied to explore novel therapeutic targets and biomarkers predicting therapeutic optimization in translational oncology. ADC, antibody-drug conjugate; bsAb, bispecific antibody or biologic; CAR-Ts, chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells; mAb, monoclonal antibody; Mut, mutation; Alt, alteration; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; ALK, ALK tyrosine kinase receptor; BRCAs, BRCA DNA repair associated genes; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; Amp, amplification; Fus, fusion; RNA-ISH, RNA in situ hybridization; UP, upregulation; IHC, immunohistochemistry; PARP, poly [ADP ribose] polymerase; DLL3, delta-like canonical Notch ligand 3; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; FGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor; TMB, tumor mutational burden.