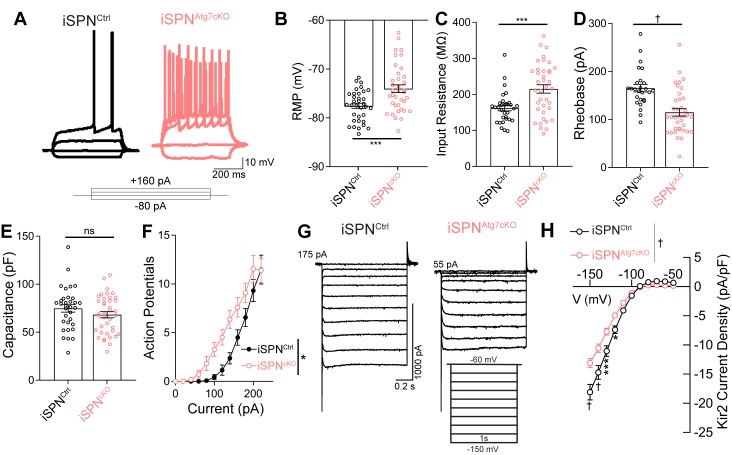
Figure 4. Loss of Atg7 leads to intrinsic hyperexcitability due to reduced Kir2 currents in iSPNs.
(A) Representative current clamp traces in iSPNs from control or iSPNAtg7cKO mice. (B-F) iSPNs lacking Atg7 display (B) depolarized resting membrane potential (t70=3.617, p = 0.0006; iSPNCtrl: n=34 (8), iSPNAtg7cKO: n=38 (9)), (C) elevated input resistance (t68=3.630, p = 0.0005; iSPNCtrl: n=32 (8), iSPNAtg7cKO: n=38 (9)), (D) decreased rheobase (t61=4.456, p<0.0001; iSPNCtrl: n=26 (7), iSPNAtg7cKO: n=37(9)), (E) no change in capacitance (t67 = 0.8096, p = 0.4210; iSPNCtrl: n=33 (8), iSPNAtg7cKO: n=39 (9)) and (F) a left-shifted current-response curve [APs/500 msec (Current x Genotype: F(13,772) = 1.538, p = 0.0983; Current F(13,772)=421.5, p<0.0001; Genotype: F(1,772) = 6.586, p = 0.0141); iSPNCtrl: n=25(7), iSPNAtg7cKO: n=36(8)]. Data in (B-F) analyzed with a two-tailed, unpaired t test. Data in (F) analyzed with two-way repeated measures ANOVA. (G) Representative voltage clamp recordings of Kir2 currents. (H) iSPNs have lower Kir2 current density in iSPNAtg7cKO mice compared to iSPNs in iSPNCtrl mice. iSPNCtrl: n = 17(5), iSPNAtg7cKO: n=25(6). Data analyzed with a two-way repeated measures ANOVA, followed by Bonferooni post-hoc test. Voltage x Genotype: F(10,400) = 13.39, p<0.0001. ns p>0.05, * p<0.05, *** p<0.001, † p<0.0001.