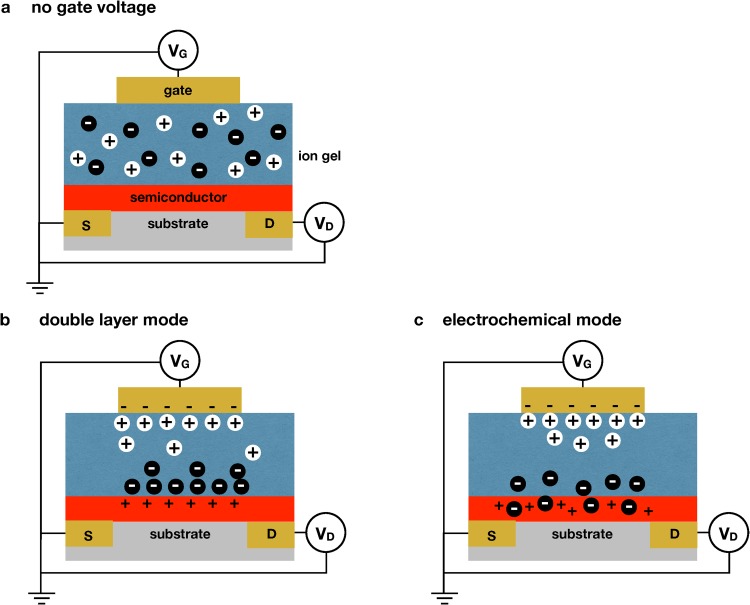
FIG. 2.
Mechanism of operation of an electrolyte gated transistor (EGT). (a) Schematic of an electrolyte gated transistor using a gel electrolyte as the dielectric in a stacked configuration. In the absence of an applied field, the ions are distributed uniformly within the gel. (b) If the ions cannot penetrate the semiconductor, application of an electric field to the gate electrode physically separates the ions within the gel to form double layers at the top and bottom of the gel. (c) If the ions can penetrate the semiconductor, application of an electric field to the gate electrode leads to the electrochemical doping of the semiconductor.