FIGURE 1.
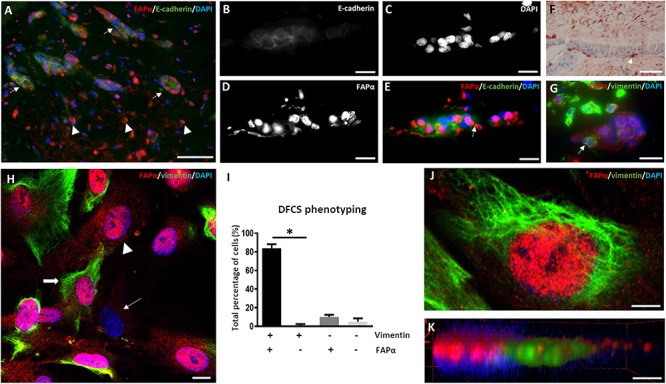
FAPα is expressed in stem cells of the dental follicle. (A) Double immunofluorescent staining in dental follicle tissue of FAPα (red), E-cadherin (green), and the nucleus (DAPI, blue). Arrows indicate epithelial rests and arrowheads point to FAPα+/E-cadherin– cells. (B–E) Higher magnification of an epithelial rest displaying E-cadherin (B), nuclei (C), FAPα (D), and the corresponding overlay (E). (F) Visualization of mesenchymal cells in the dental follicle using vimentin staining. Note the presence of a vimentin positive cell at the periphery of the epithelial rest (white arrow). (G) Double immunofluorescent staining of FAPα and vimentin showing FAPα+/vimentin– cells in the epithelial rest. A FAPα+/vimentin+ cell is located at the periphery of the epithelial rest. (H) Triple immunofluorescent staining of vimentin (green), FAPα (red), and nuclei (blue) in cultured dental follicle stem cells. Indicated cells are FAPα+/vimentin+ (thick arrow), FAPα+/vimentin– (arrowhead), and FAPα–/vimentin– (thin arrow). (I) Quantification of the different phenotypes based on vimentin and FAPα expression (n = 4; ∗p < 0.05). (J) Confocal image of triple immunofluorescent staining of vimentin (green), FAPα (red), and nuclei (DAPI). (K) 3-D volume rendering of (J) showing localization of FAPα on the plasma membrane. Scale bars represent 4 (J,K), 10 (B–E,G,H), and 50 (A,F) μm.
