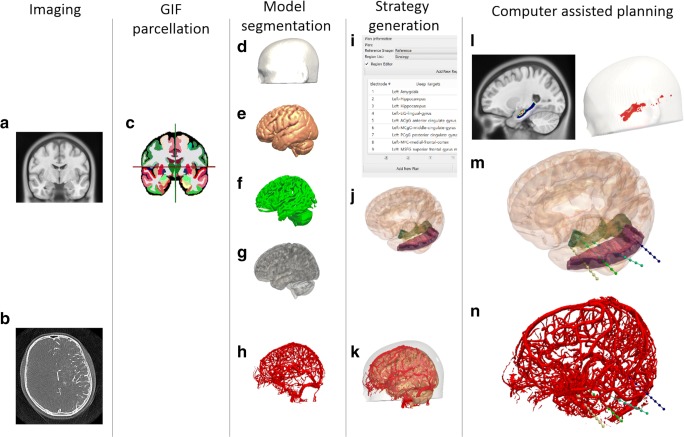
Fig. 1.
CAP image processing pipeline: imaging modalities required for CAP include a reference image (A), preferably a gadolinium-enhanced T1 image, and a vascular imaging modality (B). A whole brain parcellation (C) is generated from the T1 image. A model of the scalp (D) is generated from the reference image while models of the cortex (E), sulci (F), and gray matter (G) are automatically extracted. Vascular models (H) are derived from the vascular imaging following filter application and mesh cleaning. The implantation schema entry and target points are then selected from the whole brain parcellation (I) and brain ROIs are automatically segmented (J). In this case, amygdala, hippocampus, and lingual gyrus target regions are shown with the middle temporal gyrus as the entry region. A composite image of the scalp, brain, and vasculature is shown (K). Trajectories that exceed length, angle, and critical structure restrictions are removed from consideration. Risk maps for the target structure (only hippocampus shown) and corresponding entry zones are generated (L). CAP trajectories with shortest intracerebral length, orthogonal drilling angles, maximal gray matter sampling, and lowest trajectory risk score are provided (M). Generated trajectories also shown with vascular model (N). ROI = region of interest. Note: for clarity only temporal electrodes are shown