FIGURE 1.
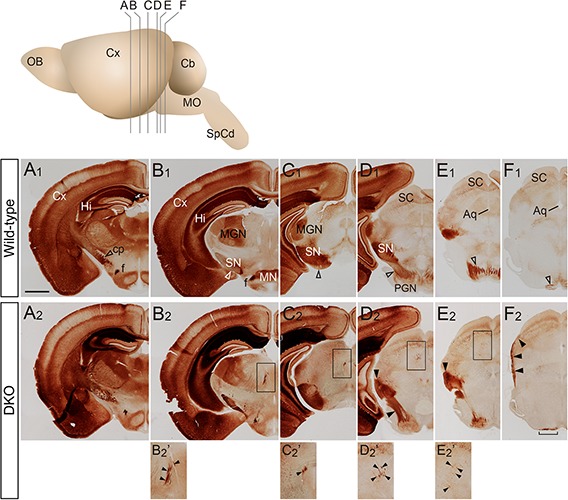
PKCγ staining images of the adult brain. (A–F) Coronal sections of wild-type (A1–F1) and Sulf1/2 DKO (A2–F2) brains through the cerebral peduncle (cp) to the pons are shown. The positions of sections (A–F) in the brain are shown in the upper panel. The open and filled arrowheads indicate the normal and abnormal projections of CST fibers, respectively. In the Sulf1/2 DKO brain, a small number of fibers projected abnormally through the thalamus to the midbrain (B2′–E2′, showing magnified images in the boxed regions in B2–E2, respectively). In the Sulf1/2 DKO brain, misdirected fibers were found on the surface of the midbrain (E2–F2) and the pyramidal tract was thinner and broader (F2, bracket) than that in the wild-type control. Aq, aqueduct; Cb, cerebellum; Cx, cerebral cortex; f, fornix; Hi, hippocampus; MGN, medial geniculate nucleus; MN, mammillary nucleus; MO, medulla oblongata; OB, olfactory bulb; PGN, pontine gray nucleus; SC, superior colliculus; SN, substantia nigra; SpCd, spinal cord. The scale bars indicate 1.0 mm (A1–F1,A2–F2) and 500 μm (B2′–E2′).
