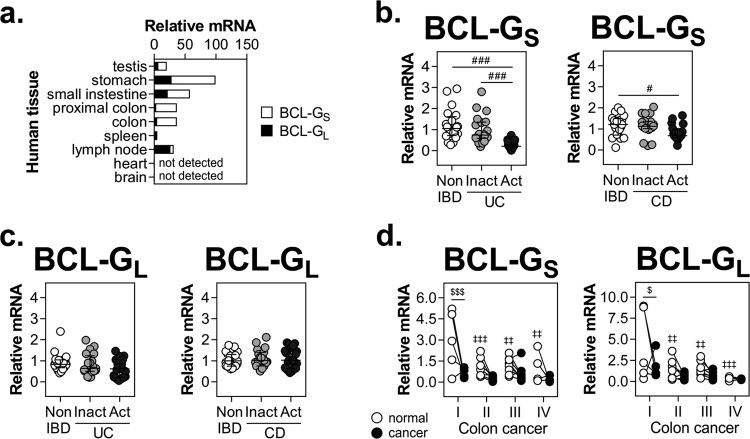
Fig. 1. BCL-G is differentially expressed in human gastrointestinal disease.
a Relative mRNA expression of BCL-GS/L measured by RT-qPCR in the indicated adult human tissues. Relative mRNA expression of b BCL-GS and c BCL-GL measured by RT-qPCR in colonic biopsy tissues isolated from non-IBD individuals (n = 20), patients with inactive (n = 20) or active (n = 24) ulcerative colitis, and patients with inactive (n = 19) or active (n = 21) Crohn’s disease. BCL-GS/L expression data in active ulcerative colitis were used for correlation analysis in Fig. 4d. For panels (b) and (c), data shown include the median with interquartile range. d Relative mRNA expression of BCL-GS/L measured by RT-qPCR in TissueScan cDNA array of 24 matched samples (normal, uninvolved colon vs. colorectal cancer) covering clinical stage I (n = 5), II (n = 7), III (n = 8) and IV (n = 4). #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test as indicated), $p < 0.05, $$$p < 0.001 (repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test as indicated), ‡‡p < 0.01, ‡‡‡p < 0.001 (repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test vs. normal colon, stage I). IBD — inflammatory bowel disease, UC — ulcerative colitis, CD — Crohn’s disease.