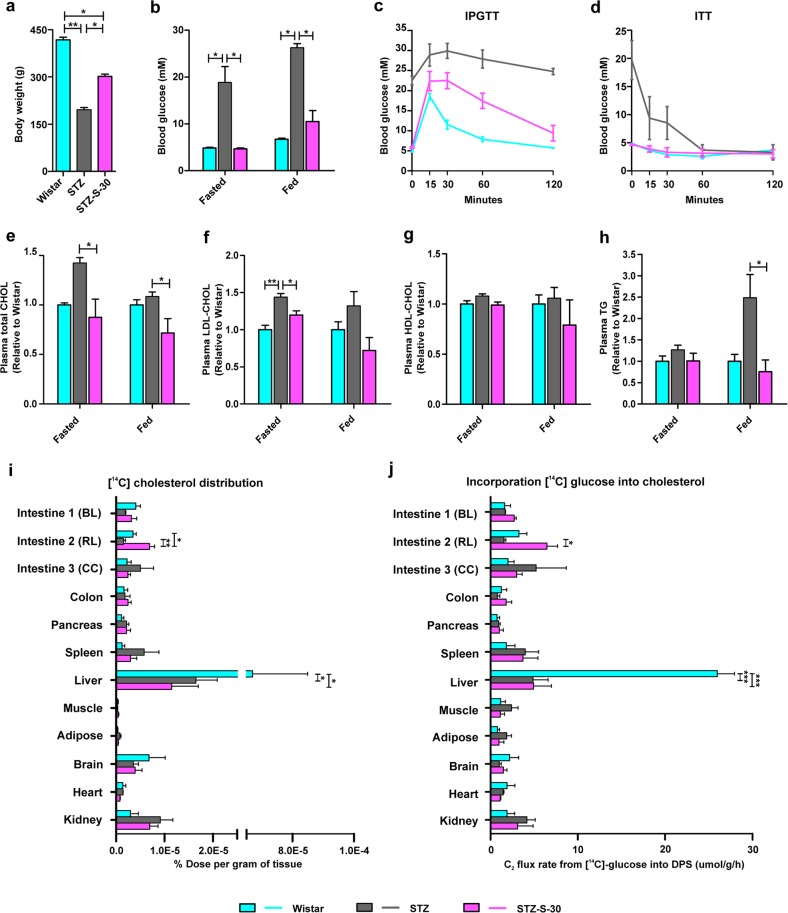
Fig. 5. Amelioration of diabetes and changes in [14C] glucose metabolism in STZ-treated diabetic rats after long-RL RYGB.
a–j Amelioration of diabetes in 30-cm RL RYGB STZ rats (STZ-S-30) was compared with both nonoperated STZ rats (STZ) and normal Wistar rats by measurement of physiological parameters 3 months postoperation. a Body weight. b Blood glucose. c IPGTT (1 g/kg glucose was injected i.p.). d Insulin tolerance test (ITT) (1 U/kg insulin was injected i.p.). e Plasma total CHOL. f Plasma LDL-CHOL. g Plasma HDL-CHOL. h Plasma TG. Rats were in fasted-overnight and fed states. i [14C] glucose was administered orally according to body weight. Three hours later, [14C] CHOL was precipitated and biodistribution was measured in the three groups. Newly synthesized CHOL from [14C] glucose was significantly increased in intestine 2 (RL) but remained low in liver. j [14C] glucose incorporation rate into CHOL. Data are expressed as µmol [14C] glucose incorporated into digitonin-precipitable sterols (DPS) per gram of tissue per hour. Data are expressed as mean ± SE. Statistically significant differences of means between groups were determined by ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (in a–h, n ≥ 4; in i and j, n = 3 for each group), where *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 for multiple comparisons among the three groups by ANOVA.