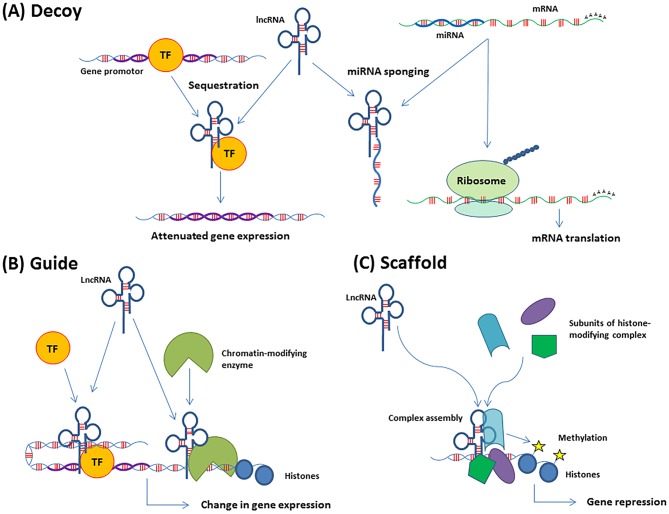
Figure 1.
Functions of lncRNAs in gene regulation. (A) Decoys can sequester transcription factors (TF) or complementary RNA transcripts, such as miRNAs (also called miRNA sponging). The consequence of TF sequestration is attenuated expression of the genes regulated by that TF. The effect of miRNA sponging is the release of the molecule e.g., mRNA which is targeted by that miRNA. The mRNA is then translated. (B) Guides recruit molecules, such as TFs or chromatin-modifying enzymes to their target areas of the genome, which leads to the regulation of gene expression. (C) Scaffolds support transient assembly of protein complexes at genomic regions, which can promote histone modifications and DNA methylation.